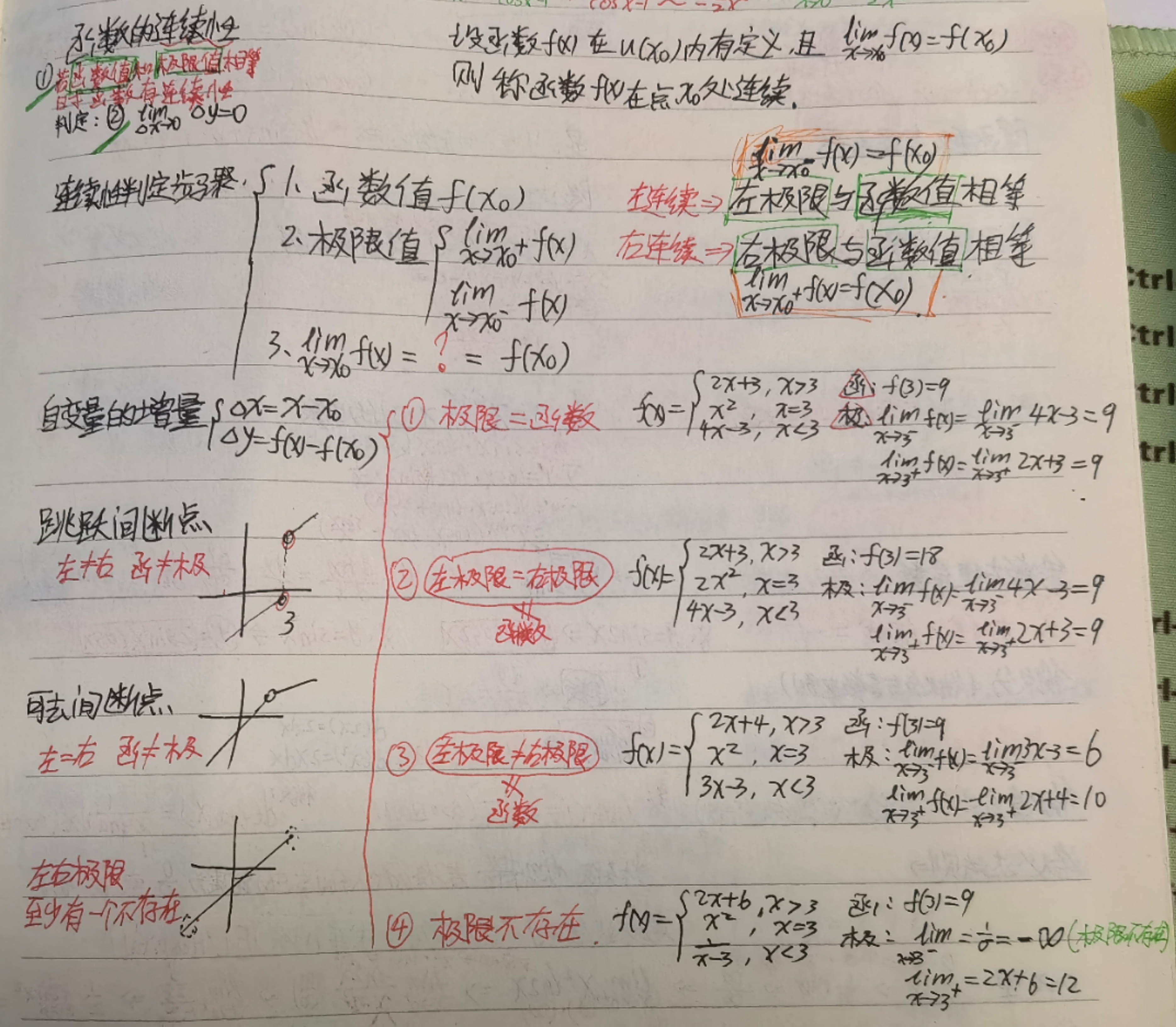
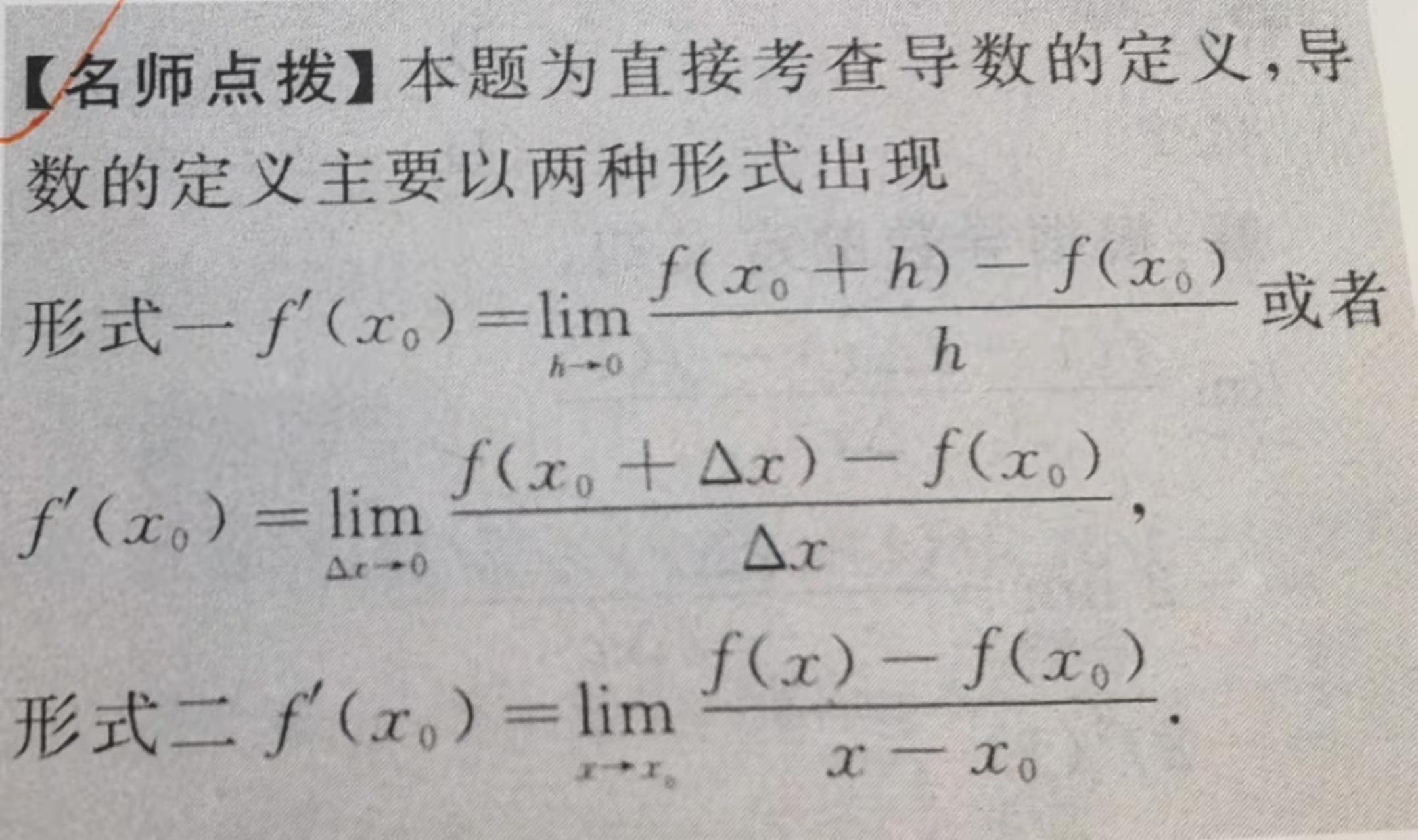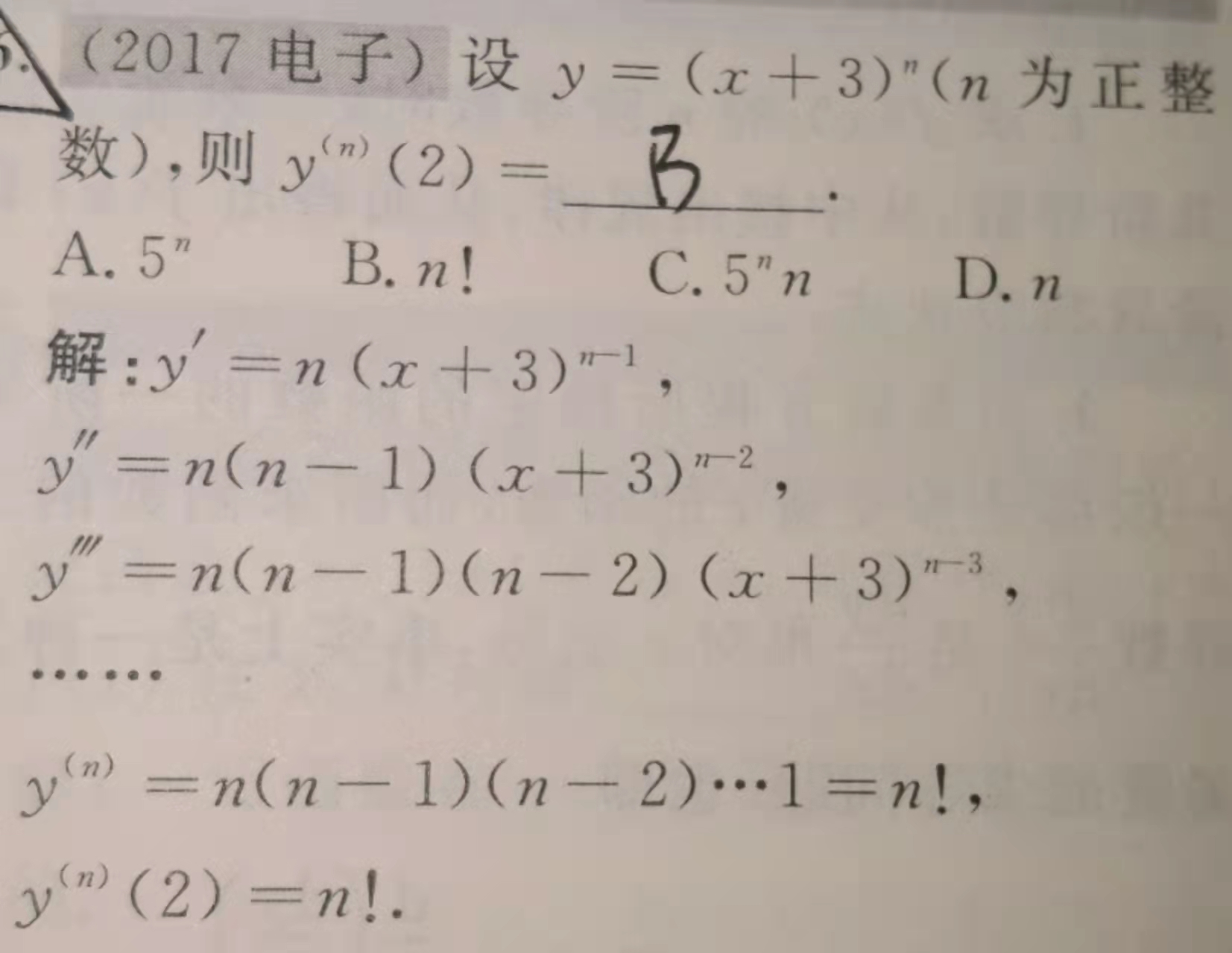计算机基础概论、进制转换、中文字符
计算机基础概论
题型:单选题、多选题、判断题、填空题、简答题、分析题、操作题、综合应用题
信息
信息是在自然界、人类社会和人类思维活动中普遍存在的一切物质和事物的属性
香农是信息论的创始人:信息是用来消除不确定性的东西
信息的单位是:bit
信息的特征:普遍性、时效性、共享性、价值相对性、载体依附性等
数据
- 数据是指存储在某种媒体上可以加以鉴别的符号资料
- 数据的分类:数值(正负号)和非数值数据(文字、图像、声音、动画、视频等)
信息与数据的关系
- 数据是信息的具体表现形式,是信息的载体,而信息是对数据进行加工后得到的结果,信息是数据的逻辑意义
- 信息的符号化就是数据,数据是信息的具体表现形式
- 判断题:有信息一定有数据(√) 有数据一定有信息(×) ∵信息的载体是数据 而数据有些是垃圾数据则不一定有信息
一定有数据 有数据一定
信息技术
- IT(Information Technology):信息技术是指人们获取、存储、传递、处理、开发和利用信息资源的相关技术
- 目前被人们称为3C(Communication、Co6mputer、Control)认证技术的是指(通信技术、计算机技术和控制技术)
- 信息技术的组成:计算机技术(核心)、通信技术(支柱)、微电子技术(基础)、网络技术和传感技术
- 信息技术的发展趋势:现代信息技术的发展趋势可概括为:数字化、多媒体化、高速度、网络化、宽频带、智能化
信息社会
- 继工业化社会以后,以信息活动为社会发展的基本活动的新兴社会形态
- 信息、物质、能量构成世界三大资源,网络成为人们生活的基础条件
计算机文化
- 人类文化发展的四个里程碑:语言的产生、文字的使用、印刷术的文明、计算机文化
- 计算机文化的真正内涵:一个人经过文化教育后所具有的能力由传统的读,写,算上升到新的高度–具有计算机信息处理能力
计算机的概念与发展
计算机概念:计算机也称之为电脑,是一种具有计算功能、记忆功能、逻辑判断功能的机器设备。它能接收数据,保留数据,按照预定的程序对数据进行处理,并提供和保存处理结果
计算机发展
- 算盘:公元六世纪左右,十进制的计算工具,算盘被称为计算机,算盘不是计数工具,而是执行珠算口诀指令的计算工具。缺点是容易出错,依赖人力限制了运算速度
- **帕斯卡计算器(补九码)**:1642年发明可进行加法和减法运算(自动)
- **莱布尼兹(传教)**:1671年发明可进行四则运算的机器,来解决进位的问题;发明了二进制
- 巴贝奇:19世纪,英国数学家查尔斯·巴贝奇最先提出通用数学计算机的基本设计思想。1822年设计了一台“差分机”。1832年,开始设计一种基于计算自动化的程序控制的“分析机”,提出几乎是完整的计算机设计方案,被称为“计算机之父”(机械的)(通用计算机之父)
- (查尔斯巴贝奇于1834年设计的分析机)是现代通用计算机的雏形
电子计算机的诞生(ENIAC:电子数字积分计算机)
- ENIAC:Electronic Numerical Integrator And Computer
- 第一台真正意义上的电子计算机
- 诞生于1946.2.14美国宾夕法尼亚大学
- 人物:莫克利、艾克特、冯·诺依曼
- 特点:1、采用十进制 2、使用电子管 3、无键盘,鼠标等输入设备,不存储程序 4、应用领域:科学计算 5、运算速度5000次/s加法 6、不是冯·诺依曼机
计算机历史人物
巴贝奇:英国数学家,差分机,分析机,有时候被称为(机械)计算机之父
莱布尼兹:德国数学家,解决进位的莱布尼兹轮,发明了二进制
布尔:英国数学家,布尔运算,逻辑TRUE对应1,逻辑FALSE对应0
香农:美国数学家,信息论创始人,信息论之父,
- 信息的定义:信息时能够用来消除不确定性的东西,提出“信息熵”符号逻辑和开关理论
艾伦·图灵
- Alan Turing, 英国数学家,计算机科学家之父,人工智能之父
- 图灵机(一种模型,并非真正计算机)(是由图灵在1936年提出的,它是一种精确的通用计算机模型,能模拟实际计算机的所有计算行为)奠定了课计算理论的基础
- 现代计算机的功能不可能超过图灵机
- 图灵机不能计算的问题,现代计算机也不可能计算
- 只有图灵机能解决的计算问题,实际计算机才能解决
- 图灵测试:由艾伦·麦席森·图灵发明
- 图灵奖:计算机界的诺贝尔奖,由美国计算机协会(ACM)于1966年设立
冯·诺依曼[美籍匈牙利科学家]
公认的电子计算机之父
冯·诺依曼工作原理(计算机五大硬件、存储程序、程序控制、计算机内部采用二进制)
EDVAC(第一台提出冯·诺依曼原理概念的计算机)
硬件系统 二进制 程序存储和程序控制
@@ ENIAC EDVAC 你!打我!
计算机发展分代
- 几个第一(==第一代计算机为二进制 第一台计算机为十进制==)
- 世界上第一台电子计算机 ENIAC
十进制(↑电子计算机的诞生),占地170平米,篮球场是420平米,占地面积约为半个篮球场- ENIAC是世界上第一台电子计算机在美国发明的
- ENIAC不是存储程序控制的计算机
- 世界上第一台投入运行的具有存储程序控制的计算机是英国人设计并制造的EDSAC 【EDVAC抢先注册】
- 第一台冯·诺依曼机
- 名称:EDSAC
- 时间:1949年5月6日
- 人物:英国剑桥大学教授莫里斯·威尔克斯
- 意义:是世界上第一台实际运行的存储程序式电子计算机
- 以EDVAC为蓝本,抢先
- 第一台商用电子计算机
- 名称:UNIVAC-1
- 第一台商用计算机是1951年产的(UNIVAC-1)
- 开发者:莫克利和艾克特,1951年
- 用途:第一台卖给了美国人口普查部用于人口普查,标志着计算机进入了商业应用时代,标志着计算机时代的真正开始,计算机从此由实验室走向社会
- 中国第一台每秒钟运算一亿次以上的“银河-1号句型计算机” 1983年,速度:每秒1亿次
- 神威·太湖之光 第一位(3,168万亿次每秒),天河二号 第二位
- 世界上第一台电子计算机 ENIAC
电晶集成大(灶)
| 年代 | 名称 | 元器件 | 存储器 | 语言 | 应用领域 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第一代(1946-1956) | 电子管计算机 | 电子管 | 水银延迟线、磁鼓、纸袋、卡片 | 机器、汇编语言 | 科学计算 |
| 第二代(1956-1964) | 晶体管计算机 | 晶体管 | 磁芯磁盘磁带 | 高级程序设计语言 | 数据处理 |
| 第三代(1964-1971) | 中、小集成电路计算机 | 集电路 | 半导体 | 操作系统会话语言 | 各个领域 |
| 第四代(1971-至今) | 大规模或超大规模集成电路计算机[微型计算机] | 超集路 | 高度集成半导体(微处理器为核心的微型计算机) | 面向对象设计语言 | 网络时代 |
| 新一代计算机 | 未来计算机 | 量光子 |
计算机特点及分类
- 计算机特点
- 运算速度快
- 计算精度高
- 存储容量大
- 具有逻辑判断能力
- 工作自动化
- 通用性强
- 计算机分类
- 根据处理的对象划分【你的对象是个魔术混合鸡】
- 模拟计算机:处理模拟数据,速度快但不精确,通用性差
- 数字计算机:处理数字数据,精度高,存储容量大,通用性强
- 混合计算机:处理数学数据和模拟数据
- 根据计算机的用途划分【专通】
- 通用计算机[家用]:解决一般问题,实用性强,如科学计算、数据处理和过程控制
- 专用计算机:用于解决某一特定方面的问题,配有专门开发的软件和硬件,用于自动化控制、工业仪表和军事领域
- 以应用为中心,软件代码小,高度自动化,响应速度快
- 根据计算机的规模划分
- 巨型机:超级计算机,常用数值计算
- 特点:运算速度快、存储容量大结构复杂,价格昂贵
- 应用领域:气象、军事、航空航天
- 大型机:金融、证券等大中型企业数据处理或网络服务器
- 小型机:中小企业、学校等
- 微型机:个人计算机PC,主要用在办公和家庭,是目前发展最快,应用最广泛的一种计算机,**运算速度快,计算精度高,记忆能力强,存储能量大,具有逻辑判断能力,数据化程度高。体积小,价格便宜,软件丰富,功能齐全**
- 工作站:具有较强的数据运算以及图像处理能力,配备多个CPU和高分辨率的大屏幕,主要面向专业应用领域:工程计算、动画制作、科学研究、软件开发、模拟仿真等
- 巨型机:超级计算机,常用数值计算
- 根据处理的对象划分【你的对象是个魔术混合鸡】
计算机的应用领域
- 科学计算:科学和工程中的数值计算,天气预报、军事国防、航空航天
世界上第一代电子计算机主要用于科学计算 - 信息管理:以计算机基础对大量数据进行加工处理,形成有用的信息,是非数值形式的数据处理,广泛应用于办公自动化、事物处理*等
*计算机应用最广泛的领域是**信息管理 - 过程控制:用计算机及时采集监测数据,按最佳值迅速对控制对象进行自动控制或自动调节,广泛应用在冶金,石油,化工,水电,机械和航天等部门
- 人工智能
- 计算机网络与通信
- 计算机辅助系统
- CAD计算机辅助设计 [Computer Assisted Design]
- CAA计算辅助分析 [Computer Assisted Analysis]
- CAM计算机辅助制造 [Computer Assisted Manufacturing]
- ==CBE计算机辅助教育 [Computer Based Education]==
- CAI计算机辅助教学 [Computer Assisted Instruction
指导] - CMI计算机管理教学 [Computer management Instruction
指导] - CAT计算机辅助测试 [Computer Assisted Testing]
- CIMS计算机集成制造系统 [Computer Integrated Manufacturing System]
- 人工智能:AI又称机器智能,主要研究智能机器所执行的通常与人类有关的功能:判断-推理
- 考点:人工智能不可能取代人类
- 计算机网络域通信
- 多媒体技术应用系统
- 嵌入式系统:以应用为中心,以计算机技术为基础,软硬件灵活变化以适应所嵌入的应用系统,用于专用计算机系统中,主要用于军事和航空航天,逐步适用于工业控制、仪器仪表
计算机发展趋势(居委[会]网之多)
- 巨型化:功能上的超级计算机
- 微型化:体积上的可穿戴式设备
- 网络化:计算机网络
- 智能化:具有模拟人的感觉和思维过程的能力,人工智能
- 多媒体化


进制及进制转换
进制的概念:用进位的原则进行计数成为进位计数制,简称进制
和进制有关的概念(**十进制 **=> D)
- **数码**:一组来表示某种数制的符号,比如二进制的0和1
- 基数:数制所使用的数码个数,常用R表示,称为R进制
- R=10,最小值0 ~ 最大值R-1
- 位权:数码在不同位置上的权值(123 = > 1×10^3-1^ + 2×10^2-1^ + 3×10^1-1^ )
- 逢十进1 借一当十
- 写法格式:238D(十进制)
(二进制 => B)
- 数码:0,1
- 基数:R=2
- 位权:1,2,4,8,16,32,64,128,256,512,1024…
- 运算规则:逢2进1,借1当2
- 写法格式:101B或(101)$_2$
- 《易经》八卦,莱布尼兹二进制,布尔,香农,冯·诺依曼
- 优点:电路简单,容易物理实现;工作稳定可靠;二进制运算简单;逻辑性强
(八进制 => O,8)
- 数码:0 ~ 8-1进制
- 基数:R=8
- 位权:R^n-1^,1,8,64……
- 写法格式:207O或者(207)$_8$
- 运算规则:逢8进1,借1当8
(十六进制 => H)
- 数码:0 ~ 16-1进制(0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,A,B,C,D,E,F)
- 基数:R=16
- 位权:1,16,256…
- 写法举例:AB7H 或 12(B)^16^
- 运算规则:逢16进1(1 + F = 1 + 15 = 10),借1当16
(1A + 1 = 1B)、(1AH = 1×16^1^ + A×16^0^ = 16+10 = 26D)
10进制的一零是10,8进制的一零是8,2进制的一零是2,16进制的一零是16
进制转换
- 任意进制转十进制 :按位权展开,再按照十进制的计算规则计算
111.1B = 1×2^2^+1×2^1^+1×2^0^+1×2^-1^
1FC.4H = 1×16^2^+15×16^1^+12×16^0^+4×16^-1^ = 508.25D
- 十进制转任意进制
- 整数部分:除基取余倒着连
- 小数部分:乘基取整顺着连(若取出后需要减去,直到小数部分乘尽)
- 注意“乘不尽”现象,一般题目会告知精确到几位(十进制都能精确的转换为二进制 ב可能乘积乘不尽’)
- 十进制四舍五入、八进制三舍四入、十六进制七舍八入

- 十进制转十六进制
- 十进制47.6875转十六进制是(2F,BH) 转换方法同上↑
- 二、八、十六进制互相转换


快速转换
@@ 字符的ASCII码十进制值为71,则其十六进制为( )
快速根据位权凑:$16^2$=256 $16^1$=16 $16^0$=1
71<256 ∴肯定有2个16进制的位权就够了 __ __ ∴ 4 7 =>$16^4$ + $16^7$ = 64 + 7 = 71



异或运算口诀:相同为0,不同为1
8 4 2 1 ($_2$) 49 7 1($_7$) 熟悉后也可以套位权 或 短除法
任何数转十进制都是位权展开
对于R进制来说,每一位上可以有 (R) 种可能,二进制每一位有0和1两种可能,十进制数每一位可以有0~9十种可能
8000 - 1 = 7FFF(借1当16【F】)
有的十进制小数不能精确转换为二进制小数**(√) 比如:0.2**
1GB = 2^10^MB,1MB = 2^10^KB
8000H = 8×16^3^D

数据存储单位及计算机中数值的表示
数据存储单位换算
计算机中的数据都要占用不同的二进制位,为了便于表示数据量的多少,引入数据单位的概念
位(bit [binary digit的缩写]),也称为比特,简记为b,是计算机存储数据的最小单位
- 一个二进制位只能表示0或1,要想表示更大的数,就要把更多的位组合起来,每增加一位,所能表示的数就增大一倍。
- 带宽,传输速率,Mbps兆位每秒 100Mbps(100兆字节,1个字节等于8位) => 除8 = 12.5
字节(Byte,简记为B,1B=8bit,计算机存储数据的基本单位)
- 微机的存储器是由一个存储单元构成的,每个存储单元大小就是一个字节,所以存储容器大小也是以字节数衡量
- 单位换算(b→1bit,1B = 8b)
- 1Bytes = 8bit
- 1KB=$2^{10}B$=$$1024B$$
- 1MB=$2^{10}KB$=$$1024KB$$=$2^{20}B$
- 1GB=$2^{10}MB$=$$1024MB$$=$2^{30}B$
- 1TB=$$2^{10}GB$$=$$1024GB$$=$$2^{40}B$$
- 1PB=$$1024TB$$
- b B kb MB GB TB PB
- 硬盘生产商是以1GB=1000MB标注的,计算机内部是1GB=1024MB
@@ 1KB等于1000个比特 (×)
字(Word,计算机处理数据时,CPU通过数据总线一次存取、加工和传送的数据称为字)
- 字长,计算机的运算部件能同时处理的二进制数据的位数称为字长,1个字位数就是字长
- 字长是衡量计算机性能的一个重要指标,==字长越长,速度越快,精度越高==
- 不同微处理器的字节是不同的,常见的微处理器字长由8位、16位、32位和64位
- “64位的电脑”是指计算机CPU字长是64位
- 63位字长的CPU必须配合支持64位的软件才能达到最佳效果,字长的性能受软件系统的约束
计算机中数值的表示—整数(定点数)
数值在计算机中如何表示和计算?
1、数值分为:整数 + 小数
2、计算机中要解决整数和小数在计算机中如何表示的问题—原码、反码、补码
3、计算机要解决编码后的数值如何进行计算的问题—补码
定位数:小数点的位置固定,如996.007 —常规计数
浮点数:小数点的位置不固定,如9.96007*$10^2$ —科学计数法
- 无符号数(整个机器字长的全部二进制位均表示数值位,不存在符号位)
表示范围:如—> 8位二进制数,有$2^8$种状态
0000 0000 ~ 1111 1111
0 ~ 255 = $2^8-1$
n位无符号整数表达范围是:0 ~ $2^n-1$ [注意:下面的是有原码的前提]
@@ 能用8位无符号二进制数表示的是(199) ∵ 0 ~ $2^8-1$ => 0 ~ 255
@@ 表示0512范围内的无符号整数,需要的二进制位数至少是(10) ∵ n=9时 0(512-1)
有符号数(把符号位数值化了的数称为机器数。最高位表示符号位,0表示正,1表示负,其余位是数值位)
==最高位0表示正,最高位1表示负==
+9 = **0**000 1001 => +0001001
-9 = **1**000 1001 => -0001001
- 机器数代表的数字,称为真值
- 考点:原码、反码、补码的相互转换
- 计算机是采用补码形式数值存储和数值运算的
- 表示范围
2、原码、反码、补码及其相互转换
负数
原码
- +9 = **0**000 1001
- -9 = **1**000 1001
- Min → 1111 1111 = —127
- Max → 0111 1111 = +127
- 缺点:0有两种表示方式:+0=00000000 -0=10000000[零的二义性给机器判断带来了麻烦] ****
- 原码的数值0有两种表示方式 +0 -0
比如:1-2=-3 → ∵ +1+(-2) → +1 -> 0000 000$1_原$ ; -2 -> 1000 001$0_原$
∴ 0000 0001 + 1000 0010 = 1000 001$1_原$ = -3
为了解决这个问题,科学家使用补码
-33的原码是 *1010 0001* 反码是 1101 1110
反码
- 原码的符号位不变,其余位取相反得到
- 反码存在的意义就是为了由原码计算补码方便
补码
- 反码+1得到
- 优点
1、在补码表示中,0有唯一的编码 0 = 0000 0000
2、用10000000表示 -128,比原码可多表示一个编码
3、利用补码可以方便地进行运算
- 补码适合运算,解决了计算机减法的问题 例如 +1-2=?
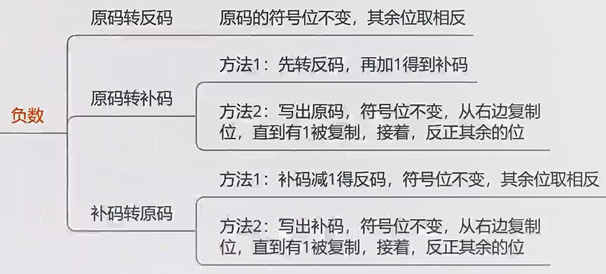
- 正数
- 原码=反码=补码
补码进行 加法 运算:符号位参与运算
☆☆ 正数:正数的原码、反码、补码都一样 ☆☆
☆☆ 负数:负数将原码的符号位保持不变,数值位各位取反再末位加1,就可以将原码转换为补码 ☆☆
@@ 机器中用数值表示的是原码+反码+补码,ASCII码西文字符:abcd…
@@ 1000 100$1_原$ → 1111 011$0_反$ → 1111 011$1_补$
@@ 求1-2的原码是:1000 000$1_原$
+1 = 0000 000$1_原$ = 0000 000$1_补$
+2 = 1000 001$0_原$ = 1111 110$1_反$ = 1111 111$0_补$
0000 000$1_补$ + 1111 111$0_补$ =1 1111 111$1_补$ “最前面的溢出数**’1’**进行舍弃”
1111 111$1_补$ = 1111 111$0_反$ = 1000 000$1_原$ = -1
@@ 在计算机内部,机器数(原码、反码、补码)的最高位为1表示该数为负数 (√)
最高位0表示正,最高位1表示负
@@ 8位二进制数值编码中,十进制“**-**9”的原码是(1000 1001)
@@ -2 -> 1000 001$0_原$ = 1111 110$1_反$ = 1111 111$0_补$ => 255 - 1 = 254
所以!!! -2 也 意味着等于 +254
@@ 负数-5在计算机中的补码是 ?
直接从原码变补码、补码变原码 口诀:从右向左复制,直到有1被赋值 其余取相反(符号位 => 第一位不变)
-5 = 1000 010$1_原$ = 1111 101$1_补$
表示范围
- 原码和反码 -2$^{(n-1)}+1$ ~ +2$^{(n-1)}-1$
- 1B 原码反码范围[-127, +127]
- 2B 原码反码范围是[-32767, +32767]
- 补码 -2$^{(n-1)}$ ~ +2$^{(n-1)}-1$
- 1B 补码范围[-128, +127]
- 2B 补码范围[-32768, +32767]
用原码表示的7位有符号二进制整数的取值范围是(-63 — +63) -2$^{(n-1)}+1$ ~ +2$^{(n-1)}-1$
3、浮点数
- 浮点数
- [组成]
- 阶码:用定点整数表示,阶码的位数确定了数的范围
- 数符(+-):占1位
- 基数:基数是隐含的
- 尾数:小数点右边的位[用定点小数表示;尾数所占的位数确定了位的精度;规定尾数的最高位为1,通过阶码来调整]
- [分类]
- 单精度浮点数:占32位,26.5作为单精度浮点数在计算机中的表示
- 双精度浮点数:占64位
- 考点:双精度浮点数表示的数的范围和精度比单精度浮点数大
- [组成]
@@ 计算机中,浮点数由两部分组成,它们是(阶码部分 和 尾数部分)
@@ 浮点数之所以能表示很大或很小的数,是因为使用了(阶码 -> 科学计数法)
@@ 在浮点数中,尾数的位数确定了位的精度,阶码的位数确定了数的范围。
@@ 用4个字节表示的浮点数11111110=> 2$^{—??} $[2的负多少次方] 11010000 00000000 00000000=> —______[负的多少] ∴阶码和尾数都为负
- 0.110101[尾数] × $2^{+5}[阶码]$
4、BCD码
二进制:0,1 —计算机采用的方式
十进制:0,1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9 —科学计数法
BCD码:一 一对应,快速转换,且精确
8421 BCD码映射关系
| 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0000 | 0001 | 0010 | 0011 | 0100 | 0101 | 0110 | 0111 | 1000 | 1001 |
十进制: 5 + 8 = 13 +0110(加6修正)
8421码: 0101 1000 = 1101
@@ BCD又称为2-10码,是利用四位二进制数表示一位十进制数
@@ 在浮点表示方法中,基数是隐含的
@@ 原码的数值0有两种表达方式,补码的数值0有一种表达方式
@@ **[负数]**将原码的符号位保持不变,数值位各位取反再末位加1,就可以将原码转换为补码(前提要说明是正负数[正数是一样的])
@@ 用原码表示的7位有符号二进制整数的取值范围是(-63 ~ +63) [最小是111 1111B;最大是011 1111B]
@@ X=(-1000101)2的反码表示=> 10111010 [最高位符号位 用1表示负数] [直接从原码变补码、补码变原码 口诀:从右向左复制,直到有1被赋值 其余取相反(符号位 => 第一位不变)]
@@ 若某带符号整数的8位二进制补码为 11110001,则该整数对应的十进制数是( 1000 1111 = > 注意第一个1是负号!!不要算入数字总和**-15**) 只有原码才可以转十进制
@@ 最高位可溢出!! 若8位进制数 结果出来了9位,最高一位溢出省略
@@ 内存单元 => 补码 原码和反码 -2$^{(n-1)}+1$ ~ +2$^{(n-1)}-1$ 补码 -2$^{(n-1)}$ ~ +2$^{(n-1)}-1$
@@ 在用原码表示整数“0”时,有“000…00” 和 “1000…00”两种表示形式,而在补码表示法中,整数”0”只有一种表示形式
@@ 通常对一个整数的补码求补码,就会得到该数的原码
@@ 正数的 原码=反码=补码
@@ “64位计算机”是指计算机的字长其越长,计算机运算精度越高
西文字符在计算机中的表示—ASCII码
(7位码)标准ASCII码 (美国标准信息交换代码)
American Standard Code for Information Interchange
概念:ASCII是国际通用的信息交换标准代码
范围:从0000 0000B到0111 1111B共可表示128个字符 【0-127】 最高位是0的128个
存储:7位ASCII码,存储占1个字符,实际使用7位,最高位为0
可打印 [不是所有ASCII字符都可以打印的,==控制字符不是打印字符==]
[控制符:LF(换行)、CR(回车)、FF(换页)、DEL(删除)、BS(退格)、BEL(振铃)等;通讯专用字符:SOH(文头)、EOT(文尾)、ACK(确认)等]
标准ASCII码比较规律
- 数字字符(0-9)、大写字母(A-Z)、小写字母(a-z)分别连续编码
- 空格符 32D (20H)
- 数字字符0 48D (30H)
- 数字字符9 57D (39H)
- 大写数字A 65D (41H)
- 小写数字a 97D (61H)
- 控制字符 < 打印字符
- 小写英文字母的编码-大写英文字母的编码=32
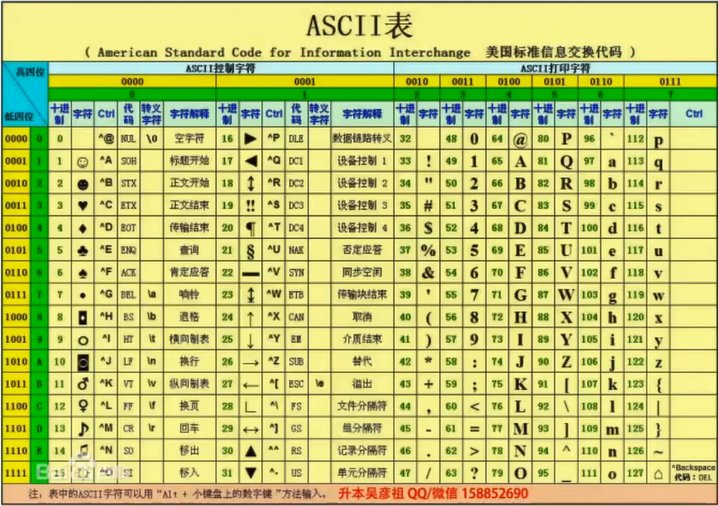
标准ASCII码表
**【65 A 97 a 48 0】**如果你要遛我(A=>65)就去(a=>97)死吧(0=>48)
竖着+横着 = 二进制
1字节 = 8bit 1KB = 1024 * 8bit
(8位码)扩展ASCII码[最高位是1 扩展码/汉字(需要连续两个开头1)]
8位ASCII码,占用1个字节,最高位为1
范围:使用1000 0000B ~ 1111 1111B,表示其他的西文字符 最高位是1的128个
中文字符最高位也是1,扩展ASCII和GB2312-80的区别在于中文字符是两个连续字节最高位都是1
@@ 在ASCII码中,存储5个西文字符的编码需要5个字节。 每一个编码占用1个字节
@@ 一个ASCII码在计算机中占用1个字节
==@@ 键盘上每个按键对应唯一的一个ASCII码 (×)==
@@ 先高四位编码,后低四位编码。已知一个数在ASCII码表中的坐标是(2,4),则其ASCII值为(66 -> B)
2 => 0010 4 => 0100 0100是高四位,0010是低四位
@@ 采用ASCII编码,最多能表示128个字符 (×) 应该是采用7位的标准的ASCII编码
@@ 一个ASCII码占据1个字节
@@ ASCII码表中字符’C’的编码1000011,则字符’G’的编码为**1000111**
C D E F G => C到G => 1000011 + 100 = 1000111
1 2 3 4 5 => 1+4=5
@@ 已知字母G的ASCII码对应的十六进制数为47H,则字母J的ASCII码对应的十六进制数为( )
G H I J => G到J => 47H + 3 = 4AH (十六进制加法 只有到了才进,不然可以用字母表示 A=10)
1 2 3 4 => 1+3=4
@@ 按照ASCII码值从大到小排列顺序 小写 > 大写 > 数字 > 空格ASCII:32
@@ 1个字符在存储的时候占用1个字节B
@@ 字符的ASCII码十进制值为71,则其十六进制为( )
快速根据位权凑:$16^2$=256 $16^1$=16 $16^0$=1
71<256 ∴肯定有2个16进制的位权就够了 __ __ ∴ 4 7 =>$16^4$ + $16^7$ = 64 + 7 = 71
@@ ASCII码表中,根据码值从小到大:空格 < 0-9 < 大写字母 < 小写字母
@@ ASCII码分为7位码[标准] 和8位码[扩展]
@@ 指令与数据在计算机内是以ASCII码进行存储的 (×) 指令与数据在计算机内是以2进制数存储的
@@ 二进制数0011 1001,若它为ASCII码[十进制值为:57;表示的(字符 )十进制为:9]
@@ 标准ASCII码可表示128个不同的字符,其中不可打印控制符字符{不可显示}有(33)个,可打印字符(95)个
@@ 根据ASCII编码原理,现在要对50个字符进行编码[表示],至少需要(6)个二进制位
解:$2^n$ ≥ 50 解得 n = 6。存储50个字符,需要50个字节 [存50条电话,需要50个位置]
@@ 在计算机中一个字节可以表示( 2位十六进制数、一个ASCII码、256种状态 )
2位十六进制数:00 ~ FF => 0000 0000 ~ 1111 1111
一个字节表示0~255 :这个简单首先理解到在内存中数据是用十六进制保存的 也就是说 00-FF
00转成十进制就是 0 FF转成十进制就是 255 所以就是 0-255
@@ 用ASCII 码可以表示汉字 (×) 它是表示西文字符的
一个汉字在计算机中占两个字节的位置 西文字符中的ASCII码表示西文字符是,用的是7位的ASCII码,为了在计算机中存储,最高位(第八位)默认为0,所以可以表示2的7次方个不同的字符;扩展的ASCII码,使用的第八位,不在默认为0,所以最多可以表示2的8次方个字符
@@ 按照ASCII码编码规则,数字符号’0’ - ‘9’的编码值为 十六进制数30-39
‘0’ ~ ‘9’ => 48 ~ 57 => 30H ~ 39H
@@ 世界上使用最普遍的字符编码是(ASCII)码,在西文字符中使用最普遍的是(标准ASCII)码
中文字符在计算机中的表示
汉字编码:采用一种科学可行的方法,为每个汉字编写一个唯一的代码,以便计算机辨认、接收和处理。
中文字符处理的基本流程:输入码 → 交换码 → 机内码 → 地址码 → 输出码
汉字的编码:
- 音码:主要以汉语拼音为基础的编码方案 如:微软拼音、搜狗拼音;特点:重码多、单字输入慢,掌握容易
- 形码:根据汉字的字形进行的编码 如:五笔字型;特点:重码少,单字输入比较快,但学习和掌握困难
- 音形结合码:自然码;特点:将音形结合起来,减少重码率,提高输入速度
- 流水码:区位码输入法 区位码输入法是一字一码,优点是无重码
输入码(外码):[特点]
- 利用键盘输入汉字时对汉字的编码
- 输入码不是唯一的,因为有音码、形码、音形结合码等不同的输入码
机内码:[GB2312-80]
- 真正的计算机内部用来存储和处理汉字信息的代码
区码 0194 国标码 2121H7E7E 内码 A1A1~FEFE
【十六进制】国标码 = 区位码 + 20;内码 = 国标码 + 80;内码 = 区位码 + 80H => 十六进制的值大于A0 [大到小 -> 内+80国+20区区位码十进制要转换成十六进制[从右到左] => 内个蛆 ] ==区位码是十进制数D、国标码是十六进制H、机内码是十六进制H==
@@ 汉字在计算机内部采用的是机内码 注意:不是国标码!!!
@@ 存储一个汉字的机内码需要2个字节
@@ 国标码GB2312-80是国家制定的汉字交换码标准
@@ 五笔型输入码属于形码
@@ 数值:补码;西文字符:ASCII码。指令和数据在计算机内部都是以二进制形式存储的
@@ 若已知一汉字的国标码是5E38H,其机内码是 DEB8
5E + 80 => DE 38H + 80H => B8H
对于GB2312来说:当某字节的最高位为1时,必须和下一个最高位同样为1的字节结合起来代表一个汉字
@@ [一个汉字的机内码] 汉字的编码 ≥ A1 在内存中若汉字以GB2312的内码表示,已知存储了6个字节的字符串,其十六进制内容依次为:6AH、B1H、D2H、53H、C8H、B4H,这个字符串中有**( 2 )**个汉字
@@ 在GB2312中,汉字的国际交换码为该汉字的区号和位号分别加32之后得到的二进制代码
@@ 汉字内码的每个字节的最高位是1,不同字体的字形描述信息存放在不同字库中。
考点1:区位码是十进制数D、国标码是十六进制H、机内码是十六进制H
考点2:区位码转国标码,先将区位码的高字节、低字节分别由十进制D转换为十六机制H,再分别+20H,就是国标码H
考点3:国际码转机内码,国标码的高字节、低字节分别+80H,就得到机内码
考点4:区位码转机内码,先将区位码的高字节、低字节分别由十进制D转换为十六进制H,再分别+A0H,得到机内码
| 汉字 | 区位码(10进制) | 国标码(16进制) | 机内码(16进制) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 中 | 5448 | 5650 | D6D0 |
| 国 | 2590 | 397A | B9FA |
| 梦 | 3546 | 434E | C3CE |
- 54D -> 36H + 20 = 56H + 80 = D6
- 48D -> 30H + 20 = 50H + 80 = D0
快速转换
@@ 字符的ASCII码十进制值为71,则其十六进制为( )
快速根据位权凑:$16^2$=256 $16^1$=16 $16^0$=1
71<256 ∴肯定有2个16进制的位权就够了 __ __ ∴ 4 7 =>$16^4$ + $16^7$ = 64 + 7 = 71
GB2312-80
一共7445个,一级汉字3755个
国际码,全称:《信息交换汉字编码字符集–基本集》
时间:1980年发布,1981年实施,我国第一个汉字编码字符集标准
区位码:全部国际汉字及符号放在94个区、每区94个位的矩阵中,区码范围是01-94、位码范围是01-94,区码和位码组合在一起,区码居高位、位码居底位,形成“区位码”
考点1:区位码是十进制数表示的
考点2:每个汉字或汉字字符都有唯一的区位码与之对应
考点3:区位码是两个字符,区码一个字符,位码一个字符
考点:区位码、国际码相互转换。
把十进制的区位码转换成十六机制,再加上2020H就得到国际码
考点:国标码GB2312是一种交换码
考点:国际码是两个字节,每个字节的最高位是0
考点:国际码GB2312使用十六进制表示 16bit
考点:中文字符国际码的取值范围是2121H ~ 7E7EH
@@ 为了解决GB2312码[国标码]和ASCII码的冲突问题,我们把国标码的最高位设置为(1),称之为(机内码[异性国标码])
GBK
全称:《汉字内码扩展规范》时间:1995年制订
两个字节表示一个汉字,向下兼容GB2312和BIG5
收录了21886个符号,包括21003个汉字和883个其他符号
GB18030
时间:2000、2005年制订,两个版本
全称:《信息技术中文编码字符集》
特点:可变长编码,采用单字节、双字节和四字节三种方式对字符编码
收录了70000多个符号
BIG5
属性:港澳台地区使用的繁体字编码方案
两个字节表示一个汉字
13053个繁体字
Unicode
中文名:统一码、万国码 时间:1994年公布
使用两个字节或四个字节表示一个字符 UCS
Unicode编码方案 UTF-8、UTF-16、UTF-32
能表示20000以上的汉字数量
乱码的问题
乱码的原因:使用一种交换码编辑文档,如果对方机器里使用的是另一种不兼容的交换码就会乱码
乱码的解决:统一使用通用的Unicode编码,或者选择安装使用同一种交换码
中文字符在计算机中的表示–输出码
又叫汉字字形码,有叫汉字字模,用于汉字在显示屏或打印机输出
使用n*n的点阵表示一个汉字的行形状,每个点使用一位二进制表示,0和1组成
根据输出汉字的要求不同,点阵的多少也不同,简易型汉字16 * 16点阵,提高型汉字24 * 24点阵、32 * 32点阵、48 * 48点阵
点阵规模愈大,字形愈清晰美观,所占存储空间愈大 1字节 = 8bit 如:16*16点阵汉字,每个汉字占用16 * 16 / 8 = 32B 故占32个字节
字库:字模点阵占用空间太大,不作为机内存储,只用来构成“字库”。字库中存放了每个汉字的点阵代码,需要显示输出时,检索字库,输出字模点阵,得到字形。
考点:汉字的字库属于输出码(字形码),不是机内码
==考点:有100个24 * 24点阵汉字,所占存储空间是多少? 100 * 24 * 24 / 8 = 7200B==
矢量字体(Vector font)中每一个字形是通过数学曲线来描述的,它包含了字形边界上的关键点,连线的导数信息等,字体的渲染引擎通过读取这些数学矢量,然后进行一定的数学运算来进行渲染。
字体实际尺寸可以任意缩放而不变形、变色,显示效果与大小和分辨率无关,因此可产生高质量的汉字输出
矢量字体主要包括Type1 . TrueType、OpenType等几类。
厂商:北大方正、makefont等
@@ 每个汉字具有唯一的内码,外码不唯一
@@ 存储一个32 * 32 点阵汉字字型信息的字节数是(128B)
@@ 中文字符集中,包含汉字数量最多的是GBK ∵ UTF-8不是专门的中文字符集
@@ GB18030 包含汉字数量最多
@@ 中文字符的范围是A1A1H到FEFEH,汉字机内码的取值范围是B0A1H ~ F7FEH
@@ 汉字系统中汉字字库里存放的是汉字的字形码
@@ 不同汉字的机内码长度是相同的 都是2个字节
@@ 区位码输入法的最大优点是一字一码,无重码
@@ 在计算机内部用机内码而不用国标码表示汉字的原因是有些情况下,国际码有可能造成误解
@@ **一个汉字的机内码与它的国标码之间的差是8080H **,国标码5E38H -> 机内码 5E38H + 8080H => DEB8H
@@ [上方考点2] 已知汉字”家”的区位码是2850,则其国标码是(3C52H) 28D -> 1CH -> +20H => 3CH
@@ 汉字的国标码由两个字节组成,每个字节的取值均在十进制33-126 ∵范围是2121H-7E7E,21 -> 2×16+1 =33,7E -> 7×16+14=126 => 33 ~ 126
@@ 一个汉字的机内码与国标码之间的差别是前者各字节的最高二进制位的值均为1,而后者均为0
@@ 若存储500个32 * 32 点阵的汉字字模信息,则需要的存储容量是64kb ∵ 500×32×32 / 8 (1字节 = 8bit) ×1024= 64KB
@@ 存储800个24 × 24点阵汉字字形所需的存储容量是( 24 × 24 × 800 )位 [==位的话不除以8,如果问字节B 就要除以8==]
@@ 计算机处理汉字时,在输入、存储、和显示阶段所使用的编码是输入码、机内码、字形码
@@ 根据汉字国标码GB2312-80的规定,一级汉字的排列顺序是按照汉字拼音字母,二级的汉字排列顺序是按照偏旁部首
@@ 为了解决GB2312码[国标码]和ASCII码的冲突问题,我们把国标码的最高位设置为(1),称之为(机内码[异性国标码])
@@ 点阵属于字形码,输入码包括括音码、形码、音形结合码、流水码
@@ 汉字国标码每一个字节的取值范围是2121H - 7E7EH
@@ 汉字输入码包括音码、形码、音形结合码、流水码
@@ 相同的汉字通过不同的输入方式外码不同,内码相同
@@ 存储400个24×24的点阵汉字字形所需的存储容量是28.125kb ;400×24×24 / 8 × 1024 = 28.125
@@ 寄存器用来临时存放参加运算的数据和运算得到的中间结果
@@ CPU通过数据总线一次存取、加工和传送的数据称为字。
@@ 计算机的运算部件能同时处理的二进制数据的位数称为字长。
@@ 汉字字形码实际上就是用来将汉字显示到屏幕上或打印到纸上所需要的图形数据。汉字字形码记录汉字的外形,是汉字的输出形式
@@ ASCII码是一种西文机内码,**一个字符的ASCII码占用的存储空间为1B**
@@ 记录汉字字形通常由两种方法:点阵法和矢量法,分别对应两种字形编码:点阵码和矢量码
@@ CPU中用于暂时存放操作数和中间运算结果的是累加器
@@ CPU中,加法运算是由**算术逻辑部件(运算器)**完成的
@@ 不同的CPU其具有的机器指令不同,因此,必须与可兼容的芯片组匹配。
@@ CPU是计算机中不可缺少的组成部分,它包含几十个甚至更多寄存器,用来临时存放等待处理数据,也担负着运行系统软件和应用软件的任务。尽管采用各种技术措施后PC机的主存速度有了很大的提高,但与CPU相比仍有较大差距,为了解决主存速度不能完全跟上CPU速度这一矛盾,PC机采用了高速缓存存储器Cache。常用的CPU由一个处理器组成,但是为了提高计算机的速度,CPU也可以由2个、10个甚至几百个几千个处理器组成
@@ CPU由运算器和控制器组成
@@ 字长是计算机一次所能处理的实际位数长度,字长是衡量计算性能的一个重要指标。字长一般是8的倍数
@@ 某显示器的分辨率设置为1024 × 768,其含义是横向点数 × 纵向点数
@@ 第一台电子计算机采用的十进制,没有采用存储程序思想
@@ 未配置任何软件的叫裸机
@@ 中央处理器:控制器和运算器
@@ 磁盘采用的是磁存储原理;光盘采用的是激光存储原理
@@ 汉字内码是真正的计算机内部用来存储和处理汉字信息的语言
@@ 微型计算机的显示系统指的是显示器+显示适配器(显示卡)
@@ ENIAC没有今天的鼠标和键盘,人们**只能通过扳动片面化大面板上的无数开关向计算机输入信息**
@@ 字节是存储信息的基本单位。bit是信息量单位
@@ ASCII称为美国标准信息交换码
@@ 每一个十进制整数都可以精确地转换为二进制整数形式,十进制小数转换为二进制方法为乘积取整,顺序排列,有可能出现循环的情况,不能精确转换 => 十进制小数0.1转换为二进制就会出现不能精确转换的情况
@@ 用于解决某一问题的一个指令序列称为程序,所有程序的集合称为计算机指令系统
@@ MIPS是计算机的运算速度单位,计算机的主频单位是Hz赫兹
@@ ASCII码是美国信息交换标准代码,它的每个字符用一个字节表示
@@ 世界上第一代电子计算机主要用于科学计算
@@ CPU从RAM中既可以读出信息又可以写入信息,但断电后所存的信息就会丢失
@@ 将磁盘上的信息调入内存时,信息写入内存储器的RAM
@@ 外部设备与总线和微处理器链接的接口电路称为适配器
@@ 把时间上连续的模拟信号转变为时间上不连续的数字信号,这个取点的过程称之为采样
@@ 计算机的算法具有有穷性、确定性、可行性的性质
@@ 在一个非零无符号二进制整数之后去掉一个0,则此数的值为原数的1 / 2倍
@@ 设内存储器的容量为1MB, 若首地址的十六进制表示为00000,则末地址的十六进制 表示为FFFF
@@ 字的位数叫字长,它是计算机一次可处理的二进制数的位数,是衡量计算机性能的一个重要指标
@@ 指令由一串二进制码组成,包括操作码和地址码两部分
@@ 高级语言可以分为两类:编译型和解释型
@@ 软件是指计算机运行所需的程序,数据和有关文档的总和
@@ 存储器由成千上万个存储单元构成,每个存储单元都有唯一的编号,称为存储单元的地址
@@ 存储程序工作原理的基本思想是存储程序和程序控制
@@ 汉字机内码是计算机内处理汉字信息时所用的汉字代码
@@ **数码**:一组来表示某种数制的符号,比如二进制的0和1 基数:数制所使用的数码个数,常用R表示,称为R进制
@@ 在计算机内一切信息存取、传输都是以二进制形式进行的集合。
@@ 一个中文字符是2个字节 2Byte=2*8bit
@@ 微型计算机的特点:运算速度快,计算精度高,记忆能力强,存储能量大,具有逻辑判断能力,数据化程度高
@@ 云计算是分布式计算技术的一种,最基本的概念是透过网络将庞大的计算机处理程序自动划分成若干个小的程序,再由多部服务器组成的庞大系统,经搜寻、计算分析之后同将处理结果回传给用户。[大的分成小的分给多个主机,同时完成 ]
@@ 1个字节 可以表示 2位十六进制 2位八进制
@@ 合并后居中(居中)、合并单元格(只合并 在最左)、跨越合并(一行一行的)
@@ 有10个盘面,每个划分出1024条磁道,每条磁道划分出2048个扇区,求硬盘空间 = 10 *1024 * 2048 * 512 = 10GB [盘面要×2]
@@ 硬盘中每个磁道中一个扇区的存储容量是512Byte
@@ 真值:是计算机内部的编码形式
@@ 操作系统的异步性是指程序的不确定性;共享性是指计算机中资源能够被多个程序使用
@@ 计算机指令的执行过程分为取指令、分析指令和执行指令
@@ CPU单位时间内一次处理的二进制位数称为字长
@@ M ASCII:77 m=77+32=109
@@ 一个ASCII码占用 1字节
一个汉字机内码占用2字节
一个字节可以表示2十六进制位
与同1(张雨桐是1) 或11(喝11)
与(&)(逻辑乘) 运算 0&0=0, 1&0=0, 1&1=1
或(|)(逻辑加) 运算 0|0=0, 0|1=1, 1|1=1
非() 运算 非运算即取反运算 1变0, 0变1相同为0,不同为1~ 运算 0^0=0, 0^1=1, 1^1=0
异或(^)
@@ 数值∈[0,R-1]
2023.3.14计算机题目
UPS不断供电系统(电池)
A盘 B盘用于古代的软盘
@@ 把连续的模拟信号按照一定的频率进行采样,得到一系列有限的离散值
@@ 存储载体 + 传输载体
@@ 存储器Cache:解决cpu和内存之间速度不匹配
@@ 从快到慢:寄存器、Cache、RAM、硬盘、U盘
@@ ROM只读存储器、PROM可编程只读存储器、EPROM擦除…
@@ MIPS运算速度
@@ 数据和信息关系,先有数据,再获取信息;文字图形图形视频 -> 信息;
@@ 世界上第一款 商用计算机
@@ 计算机采用二进制的原因:①电路简单 ②简化运算 ③可靠性 ④逻辑性 ⑤通用性
@@ 冯诺依曼体系的设计思想:程序存储和程序控制
@@ 利用区位码输入汉字时,输入十六进制题目给出不用转换代码”10 23 24 19”
==① 输入了 2 个汉字一个字节可表示2位十六机制[10,23,24,19四个字节],共用了 4 个字节==
② 填写出小李输入的汉字在计算机内部的存储形式
已知区位码 1023, 2419,求 机内码十六进制 => AOAO AOAO => BOC3 C4B9
[大到小 -> 内+80国+20区区位码十进制要转换成十六进制[从右到左] => 内个蛆 ]
机内码 取值范围 AOAO-FEFE
H
① 西文字符 ASCII码 (标准 扩展) 【复习】大小排序(在Excel内不区分大小写)
② 整数 采用 补码
正整数 原、反、补相同
负整数 补 是符号不变,原码取反+1
③ 汉字 采用 机内码 = 区位码 + 2020H + 8080H [要注意10进制转换16进制]
④ 浮点 采用 阶 和 尾
+0.377 × $10^8$ +是阶符 8是码 0.377尾数 10->R是基数 8是指数
指数是范围 尾数是精度
@@ 虚拟地址是用户编程可使用的地址
@@ 操作系统通过逻辑设备名中断号识别I/O设备
@@ 网桥就是交换机
@@ 文件有只读属性指的是 文件中的内容被保护,文件可以被删除,移动,保护
@@ 内存中数据进入高速缓存 再进入硬盘;硬盘中的数据;[CPU到Cache 内存到CPU]??
硬盘内部是磁盘到柱头 外部磁盘缓存 ->系统总线
外部:高速缓存 再进入内存
内部:硬盘的磁头到硬盘的高速缓存 [硬盘内外之间有自己的高速缓存]
铭升练习册填空题
@@ 基本ASCII码包括128个不同的字符
@@ 不少微机软件的安装程序都具有相同的文件名,Windows系统也如此,其安装程序的文件名一般为Setup.exe
@@ 用24 × 24点阵的汉字字模存储汉字,每个汉字需要72字节 24×24÷8
@@ CPU的性能指标中,CPU的时钟频率称为主频
@@ 微型计算机中最大最重要的一块继承电路板称为主板
@@ 光盘的读写设备是光盘驱动器
@@ 计算机的工作原理可以概括为存储程序和程序控制
@@ 指令的执行过程包括取指令、分析指令和执行指令
@@ 输入设备、输出设备和外存储器合称为外设
@@ 存储器被划分为多个存储单元,每个存储单元都被赋予一个唯一的编号,这个编号被称为存储单元的地址
@@ 在Windows中,应用程序中”编辑(E)”菜单,可用Alt+E
@@ 每当运行一个Windows的应用程序,系统都会在任务栏上增加一个按钮
@@ 若想调整音量的音量大小,可用双击任务栏上的音量
@@ 在win7中,磁盘清理程序通过删除无用文件来帮助释放硬盘驱动器的空间;磁盘碎片整理整理程序重新安排计算机硬盘上的文件、程序以及未使用的空间。以便程序运行得更快,文件打开得更快
@@ 按Alt+F4键可以关闭窗口或退出应用程序;如果某个应用程序不再相应用户的操作可以同时按ctrl+shift+esc
@@ 若想删除某个输入法可以选择”控制面板“中的区域和语言选项
@@ 在资源管理器窗口中,显示资料的方式有:**(超大,大,中,小)图标、平铺、列表、内容、详细信息**
@@ Windows的回收站是硬盘中的一块区域
@@ 按Alt+PrintScreen键可以复制活动窗口的图形到剪贴板
@@ 用于解析域名的协议是DNS
@@ 将文件从FTP服务器传输到客户机的过程称为下载
@@ 网址www.pku.edu.cn中pku.edu.cn是在Internet中注册的域名
@@ 一般拨号入网,是指通过公用电话系统PSTN与Internet服务器连接
@@ 提供不可靠传输的传输层协议是UDP
@@ Internet主要由四大部分组成,其中包括路由器、主机、信息资源、通信线路
@@ 构成局域网的基本构件有PC机、传输媒体、网卡(网络适配器)、网络连接设备、网络操作系统
@@ 被称为最早的网络是ARPAnet网
@@ 开放系统互联参考模型简称OSI参考模型
@@ 开放系统互联参考模型OSI/RM
@@ 中继器=集线器:放大信号;
网桥=交换机:寻址、存储、转发;
网关=路由器:分组交换
@@ Hub的中文名称是集线器
@@ 双绞线可以分为屏蔽抗电磁干扰强和非屏蔽两类
@@ 在OSI参考模型中,物理层传送数据的单位是比特
@@ 广域网中广泛使用的信息交换技术是分组交换技术
@@ 根据宽带来分,计算机网络可分为宽带网和基带网PC发出来的未经过调制的原始信号
@@ 网络中数据传输形式有线路、报文、分组交换
@@ 计算机指令的合集成为程序
@@ 把源程序翻译后的机器语言程序叫做目标程序
@@ 多媒体技术的基本特征主要有多维性、集成性、交互性
@@ word域代码和域结果,按Shift+F9键可以实现相互切换
@@ word中,图片插入有两种方式:嵌入方式和链接方式
@@ 在Excel中,若只需打印工作表的一部分数据时,应先选定打印区域
@@ 所谓文件是指逻辑上具有完整意义的信息资源程序和数据的集合
@@ 窗口转换Alt+Tab或Alt+Esc
@@ MS-DOS是微软公司开发的磁盘操作系统,是一种在个人计算机上使用的命令行界面操作系统
@@ windows支持的文件系统有FAT16、FAT32和NIFS
@@ Internet是全球最具有影响力的计算机互联网,也是世界范围最重要的信息资源网
@@ 任务管理器有两大功能:一是显示当前打开的应用程序、进程、CPU和内存资源消耗情况
@@ 标准ASCII码是用7位二进制位来表示128个字符
@@ 每个汉字的机内码需要用2个字节来表示
@@ 标准ASCII码是用7位二进制进行编码
@@ 在计算机中,对既有整数部分又有小数部分的实数,使用浮点数表示
@@ 文件是一组按一定格式记录在外存中的一组相关信息的集合
@@ Excel是电子表格应用程序
@@ 计算机内部件传输信息的公共通路称为总线,一次传输信息的位数称为总线的宽度
@@ 数据总线宽度:决定了字长; 地址总线宽度:决定了访问内存的容量
@@ 某台主机属于国内企业系统,其域名应以com.cn结尾
@@ GIF LZW是运用了无损压缩算法 但是有损压缩
@@ 分布式 是 大任务划成任务;分时 是 轮流使用主机资源
@@ 一个进程 包括了 多个线程;资源分配是按进程;资源调度是按线程
@@ IPV6采用冒号十六进制 IPV4采用点份十进制
@@ 快捷方式是指针
@@ 卸载程序会修改注册表;注册表存储着文件与程序的关联关系
@@ 文件处理软件属于应用软件
@@ 用户控制等在文件 选项中
@@ 视图选项卡:新建窗口、拆分窗口 => 在多个窗口中编辑一个文档
@@ 拆分 将窗口拆分成 上下 两个部分,方便编辑长篇文档
@@ 在一个窗口的结果中,显示在所有的窗口中,像任何情况下,只能有一个编译窗口
@@ 文件菜单下显示 最近打开过的文档的快捷方式;视图菜单 切换窗口:显示所有当前打开的文档,可选择 活动文档
@@ 单间头 双箭头
@@ 导入图片有两种方式:文件导入 + 剪贴板导入
@@ 连击两次工具条中的斜体按钮,则这句话的字符格式不改变
@@ 默认的整篇文档叫节
@@ word中建立的表格都是绘制的表格
@@ 图形对象可以同时添加阴影效果和三维效果
@@ 灰色不可用 黑色可用
@@ 工作表是工作簿的基本构造块
@@ 文件 信息 保护工作簿 命令:保护工作簿
“结构“:增加、移动、删除、重命名工作表
“窗口“:工作簿窗口的大小和位置
@@ 保留最近的24次内容
@@ 演示文稿不是幻灯片 演示文档由幻灯片组成
@@ 幻灯片可以设置页脚[可插入日期和时间]
@@ 幻灯片中对象的效果可以自定义
@@ 幻灯片打包时连同播放软件一起打包
@@ PPT可以插入EXCEL表格 用链接
@@ 多媒体技术中使用数字化技术,与模拟方式相比经济,造价低
@@ 软件发展的三个阶段:第一阶段最初运用于科学与工程计算,使用低级语言编制程序;第二阶段先高级程序语言编制程序,并产生了操作系统和数据库管理系统;20世纪80年代初期,出现了”软件危机”。第三阶段为适应开发大型软件的需要,提出了”软件工程”
@@ 网关:运行在路由器中的 协议转换软件 称路由器为网关
@@ 黑客或病毒攻击
@@ 最大化和还原不能同时出现
@@ LWZ使用了无损压缩技术
@@ CD-ROM一般即指光存储介质,也指CD-ROM驱动器
@@ 最多显示50个最近打开的文档
@@ RSA不对称加密 DES算法属于加密技术的对称加密
@@ ASCII码是7位二进制编码
@@ H字母是48H J是4AH
@@ 磁盘分区NTSF
@@ 计算机的存储器由千千万万个小单元组成,小单元是1位二进制
@@ Alt 交替换挡键
@@ Alt+回车 可以打开属性对话框
@@ 计算机科学的奠基人图灵
@@ 某次数据传输共传输了10000000字节数据,其中有50bit出错,其中误码率为
50/(10000000×8)=6.25×10$^{-7}$
@@ 数据=信息+冗余数据
@@ 空格 逻辑与 + - 逻辑非 |逻辑或
@@ 二八十六转十进制 都可以用按位权展开
@@ 服务器作用:管理网络资源,提供网络服务
@@ Win7里不允许更改网络图标
@@ 硬盘使用前先分区 再格式化
@@ 数字相同 进制越小 数值越小
@@ 有符号的值取值范围 0 11111大 - 1 00000小
@@ 无符号的值取值范围 0 00000 - 1 11111
@@ 一个字符的ASCII,占用二进制数的位数是8位
@@ 一个字符的ASCII编码,占用二进制位数是7位
@@ 文本框默认浮于文字上方
@@ 计算机的通用性使其可以求解不同的算术和逻辑问题,这主要取决于计算机的可编程性
@@ 一个有符号的整数,用一个字节的二进制表示其内容分别是10100000 = -41 和 11010111 = -96
@@ 打开任务管理器,在窗口中,进程选项卡提供进程信息,性能选项卡提供CPU和内存利用率,联网选项卡提供了网络使用率和状态信息,用户选项卡显示了登录用户信息