关于各种从句,有一个浅显易懂的规律:它在句子里面是什么成分,就是什么从句。
定语是用来修饰、限定、说明名词或代词的品质与特征。
定语翻译汉语为”…的”
单独一个的形容词会放在名词**前面**
lovely cat
定语从句,放在名词后面 → 形容词性从句 [用一次词表达不了,要用多个词/句子]
定语从句公式:**名词[先行词] + 连接词 + 句子**
The book that I bought yesterday.
这本他写的书很悲伤。
The book ___ is sad. => The book that he wrote is sad.
连接词 + he wrote[缺少宾语 == 连接词 == 名词]
定语从句
修饰限定名词,是一个句子,但是跟形容词一样一样的 …的
定语从句[戴帽子]:作定语词长 有动词,白字的
先行词:被定语从句所修饰的名词、代词
人还是物,缺不缺宾语?
| 先行词 | 关系代词 | 句中所作成分 |
|---|---|---|
| 人 | who[主格做主语] | 主语或宾语 |
| 人 | whom[宾格做宾语] | 宾语 |
| 物 | which | 主语或宾语或表语 |
| 人或物 | that | 主语或宾语或表语 |
| 人或物 | whose[誰的] [人的/物的] | 定语/无成分 |
先行词 = 成分 = 关系代词
关系代词指代先行词; 可以在从句中充当主,宾,表的成分; 连接主从句。
who, whom, whose
who:主格,在从句中作主语,只可指人
whom:宾格,在从句中作宾语,只可指人
whose:属格,在从句中作定语,可指人也可指物
l know the boy whom he is talking with. 宾语
He has a friend whose father is a doctor.
找主干首先先找动词
The girl (who is sitting over there) is my girlfriend.
The man (who you主语 talked谓语 to缺少宾语 just now) is my teacher.
The book (which you bought缺少宾语 last week) is very useful.
This is the little girl (whose缺少定语 parents are both teachers.)
==不能用that的情况==
- 非限制性定语从句不用that,要用which或who
- 介词+which (whom) 引导的定语从句不用that
- 先行词为that或those不用that,要用which或who
- 当先行词为人称代词he, they 或one(s), anyone, nobody等词时不能用that,要用who
==不能用which的情况==
- 先行词是all、much、few、little、everything、anything、nothing等不定代词时
有什么你想购买的吗? Is there anything that you want to buy?
这些是我看过的照片. These are all the pictures that I have seen. - 先行词既有人又有物时
我父亲和他的老师谈了很多他们还能记得的人和事。
(My father and his teacher talked a lot about things and people) that they could remember. - 先行词被形容词最高级或序数词,或the only, the very, the last等修饰时
我读过的第一本英文小说是《双城记》。
The first English novel that l read was A Tale of Two Cities.
这是我看过的最棒的英文电影。
This is the best English film that l have ever seen. - 当主句是以who或which开头的疑问句时。
站在房子前面的那个女人是谁?
Who is the woman that is standing in front of the house?
哪一个是这所学校校长工作的办公室?
Which is the office (that) the principal of the school works in?
@@ 做题技巧:**找动词、画成分、分析成分、看先行词**
考试的时候直接从横线开始看!【不缺成分才用】
时间:when 地点:where 原因:why
关系副词:whose[谁的]
when、where、why = 介词 + which [介词是跟前面的名词(先行词)固定搭配得来的]
We never forget those happy days when we studied in school.
=> We studied in school on those happy days.
This is the restaurant where we celebrated your birthday last year.
=> We celebrated your birthday last year at the restaurant.
This is the reason why I study hard.
=> I study hard for the reason.
| 先行词 | 关系副词 | 句中所作成分 |
|---|---|---|
| 表示时间 | when | 时间状语=介词+which |
| 表示地点 | where | 地点状语=介词+which |
| 表示原因 | why | 原因状语=介词+which |
The new phone (for which you have been waiting) will be in your hands soon. 【看waiting 和 The new phone之间所需要的介词是什么】
跟你说话的人是一个老师
The man (to whom you spoke) is a teacher. 【you spoke to the man】
“介词 + which(whom)” 结构中用什么介词可以根据以下原则来决定:
- 根据介词与先行词的固定搭配来选择:
l will never forget the day on which Tony came to this company. (on the day在那天)
我将永远不会忘记托尼来这家公司的那一天。 - 根据介词与从句谓语动词的固定搭配来选择:
This is the phone on which he spent 6,000 yuan.
(spend some money on sth. 花费在…上) - 根据介词与从句中形容词的固定搭配来选择:
The issue with which all of us are concerned will be discussed tomorrow.
( be concerned with sth.关注;担心)
我们所有人都关注的问题将在明天被讨论。 - 根据句意来选择:
This is Tom’s computer, without which he couldn’t finish his work.
这是汤姆的电脑,没有它他就无法完成自己的工作。
- 从句只是对先行词的附加说明
- 去掉从句,句子的意思仍然完整
- 从句和主句之间用逗号隔开
- 引导词有: which、who、whom、where、when、as、whose
Beijing, [which has been China’s capital for more than 800 years], is rich in cultural and historic relics.
北京是中国八百年之久的古都,它有着丰富的文化和历史遗产
She passed the exam, which made her parents extremely happy.
【有逗号】先行词即可以是一个词,也可以是一个句子
He put off the party until June, when he will be free.
除了that以外,其他的关系代词和关系副词用法照旧
as引导的非限制性定语从句
可以放在主句之前或之后,甚至插入主句中间:
As is known to all, China is a developing country.
Little children, as is often the case, rely more on their parents.
固定搭配:
==as is often the case (情况常常如此)
as often happens (正如经常发生的那样)
as is known to all/as we all know (众所周知)
as was expected (正如预料的那样)
as is mentioned above (正如上面提到的那样)==
@@ The factory,(which we’ll visit缺少宾语 next week,) is not far from here.
①确定从句是定语从句{翻译成汉语是”…的”,能找到先行词)
②排除错误选项:
what不能引导定语从句
it、this、those、these不能引导从句
③分清是限制性还是非限制性(根据逗号)
that不能引导非限制性定语从句
④根据先行词的意义,分清是指人、还是物,表示时间、地点还是原因。
@@ I like the house (whose缺定语 windows face south.)
@@ This is the dictionary (which my mother gave me缺宾语 for my birthday.)
@@ The train on which (she was traveling不缺成分) was late. 用关系副词 / 介词 + which
@@ The young lady whom (we met yesterday缺宾语) is our new math teacher.
@@ We are going to spend the Spring Festival in Guangzhou, where my grandparents and some relatives live(in). [where / in which]
@@ that 不能用于非限制性定语从句
| 先行词 | 关系代词 | 句中所作成分 |
|---|---|---|
| 人 | who[主格做主语] | 主语或宾语 |
| 人 | whom[宾格做宾语] | 宾语 |
铭升教育↓
定语从句是修饰/限定名词的 被修饰的词为先行词
连接代词 指代 代替了成分;连接副词 没有起作用不代替任何词
I like quiet定语 music.
I like music (that is quiet)定语从句 【that 后面 跟is 因为music是单数】
I know a girl修饰限定为先行词 who likes red.定语从句
帽帽词[不包含what噢]:who whom when where why that which whose
I like music (that is quiet)定语从句 后面不完整 is quiet 缺主语,所以用that
连字诀:先行词能不能与后面连得上;能直接连上的就是关系代词;music is quiet
关系代词:who which that
| 先行词 | 关系代词 |
|---|---|
| 人 | who that whom宾语 |
| 物 | which that |
| 人和物 | that |
Mary is a beautiful girl. is a girl 能连上 变定语从句时用关系代词【缺成分】
Mary is girl who is beautiful.
Mary is a girl,Mary has long hair.
Mary is a girl who has long hair.
Mary who is a girl has long hair.
I have an apple. An apple is red.
I have an apple which/that is red第一句是主句
An apple which I have is red第二句是主句
I have some friends. Some friends like sports.
I like the movie. The movie is exciting.
The woman is a teacher. The woman lives next door.
The woman who/that lives next door is a teacher.
The woman is a teacher who lives next door.
关系代词在句子中充当主语/宾语
有疑问句只能把疑问句为主句!!
==引导词扮演后面的主语[头]时,不能省略;;跟后面引导的句子有关!!!==
==定语从句中包含it的全是错误的!!==
==This is the card which/that/whom做宾语[可以省略] I’ve just received.== [砍了腿腿可以活 也可以用whom因为它引导做了宾语!]
==This is the film star who/that做主语[不可以省略] is very popular in China.== [不可以用whom 因为是宾语的 不可再加it]
whose用于 “…的” 作定语从句的定语
前名词 后名词 中变的 能够连上为whose
I know the girl whose mother is a teacher
as和which都可以引导非限制性定语从句,但as引导的非限制性定语从句可以位于主句之前或之后,甚至可以插入主句中间,且as有”正如,正像”的意思,而which引导的非限制性定语从句只能位于先行词之后
==as放在开头、正如…知道的/whose 不轻易在选项中出现,若出现则80~90%是答案==
as用在有效单词的第二个空,答案有as,可能是倒装,As换成Although
as放在句子中间靠后有as时,去前面寻找固定搭配。是则是 same,such,so + as
so + adj + as;As we all know(正如我们知道的是);
★★ 有时只能用that,不用which的六种常见情况 ★★
- 当先行词是:all, any, few, little, none, anything, everything, nothing, everybody, nobody, everyone, no on 或 被它们修饰时。
That’s all that I know - 当先行词被形容词最高级或序数词修饰时 [指代非常明确 那个!!用that]
That is the most interesting book that I have ever read. - 当先行词有the very, the only, the same等修饰时 [指代也很明确,是那一个!! 用that]
- 当主句以who或which开头时,定语从句关系词用that,而不用which和who
- 先行词同时包括人或物时,关系词用that
- 当主句是There be句型时 [那有个…啥!!那 特指用that]
★★ 只能用which 不能用that的情况 ★★
关系代词前有介词[whom/which] 先行词是人的用whom,先行词是物用which 第四题下方
前面有逗号[whom/which] 先行词是人的用whom,先行词是物用which
先行词本身是that
as引导非限制性定语从句
Those后面只能用who [指的是人!]
@@ The man whose hair is white is his grandfather.
@@ Tom is **one of **the boys that are (be) from the USA 有the用单数,没有the用复数
@@ He is one of the students who has made great… one前面没the用复数 有the用单数
@@ The boy with whom John spoke is my brother
这就是(救了那个孩子命的)**医生 **[先找主谓宾]
This is the doctor who saved the child.
(正在跑步的)那个人是(我的
定语)叔叔
That man is my uncle who is running.
The man who is running is my uncle.
我喜欢(可以随之而唱的)音乐
I like the music which I can sing to
住在隔壁的那个女的是一名教师
That women is our teacher who lives next door.
定语从句高阶版[关系副词]
连不上就加介词连接
The city in which she livesin is far aways.
The city which she lives in is far aways.
The farm on (which we worked ten years ago) is beautiful. 介词后面有帽帽词
we worked on the farm【在土地上养】
This is the tree under which (we used to play games).
The money with which you were to buy dog food is gone.
==介词:用:by(抽象概念和方法[交通工具/手]) with(实际的事物东西) in(语言和原材料)==
==时间:by年月日小时分钟 后面可以跟数字[上涨了多少] on一天 at时间点==
坐在桌子前学习用at
We thought you were a person from/for/about whom we could expect good decisions.
Air, without which man can’t liveair, is really important
This is the man who/that/whom/可省 I learned the news form. [连字诀]
This is the man from whom I learned the news.
This is the room which/that we lived in last year.
This is the room in which we lived last year.
Do you like the book on which she spent $10? 时间金钱 Spend后面直接可以接金钱和时间 有必要再加on
I will never forget the days that/which we spent together. [可以直接连字诀]
==@@ 表示方式方法时,前面先行词是the way介词是in which 此时的in which可以换成that 且that可以省略==
==@@ 先行词是the place 后面是where,此时the place 可以省略==
@@ I don’t like the way you speak to her.==定语从句:一强二定连字诀[直接/加介词也连不上]三名词==
@@ ==主谓一致:一单二被三时态== 去前面找信号词找主语 the one of + 单数 one of + 复数
That is one of those books that are worth reading
@@ This is the only one of the students whose handwriting主语 is the best.
@@ There was nothing we could do to prevent the accident.
any用于否定和疑问 some用于肯定
@@ Is this school名词不可裸奔the one that we visited three years ago? [名词性从句] [we visited缺了宾语]
this school is
@@ Is this the school / we visited three years ago? we visited the school 可省略
疑问变陈述 this is the school …
@@ During the week followed/that followed he tried to collect materials for his article.
做定语的非谓语 只有一个词的时候 要前置放在修饰词前;敢后置的一般都是两个或两个以上的词
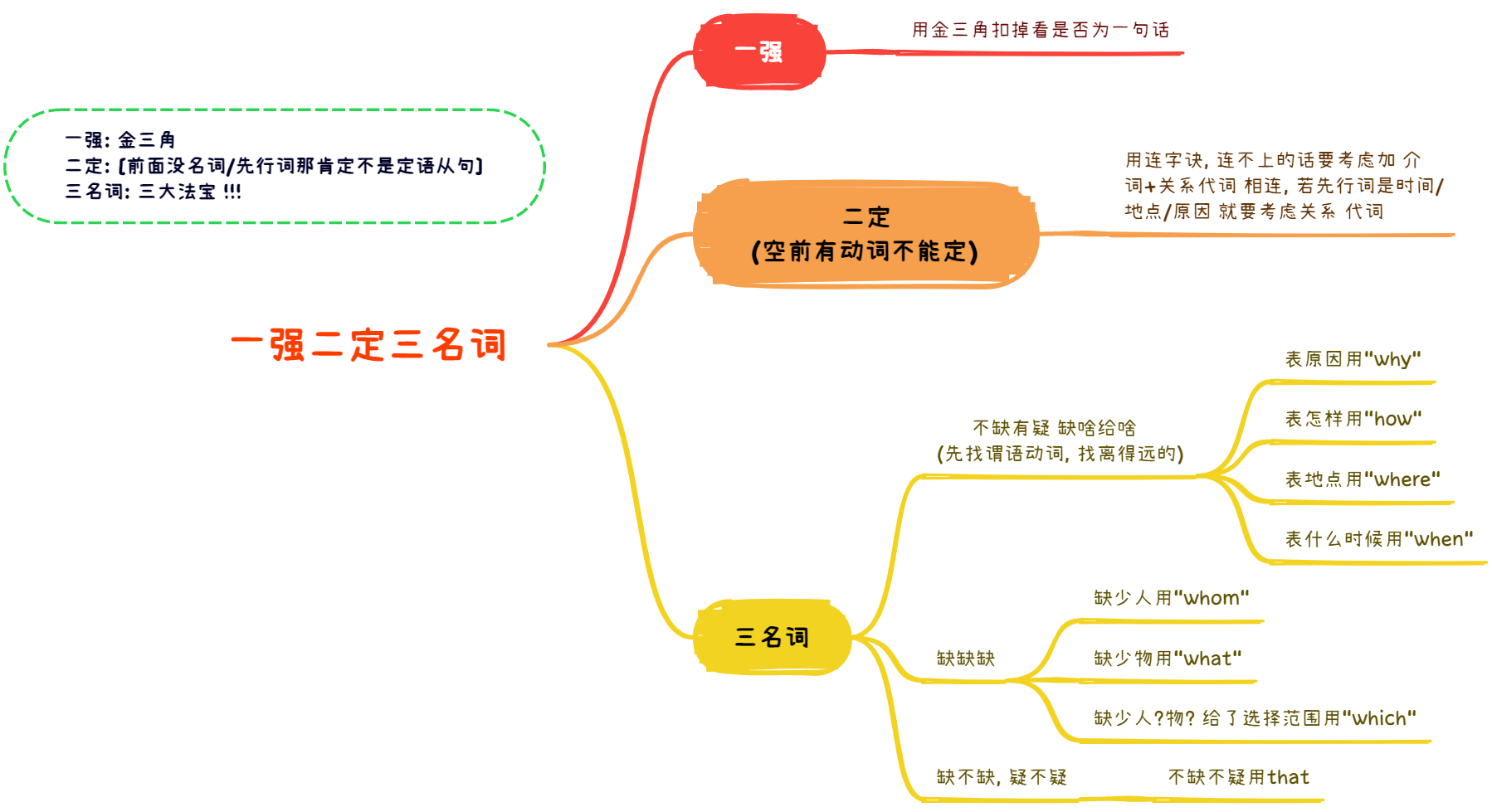
★★★★★ 名词+介词+关系代词 ★★★★★ [介词后面不接that]
有逗号没连词 帽帽 !不是whom 就是 which
连字诀连不上 要考虑加介词+关系代词相连 若先行词是时间/地点/原因 就考虑关系代词
Recently I bought an ancient Chinese vase, the price of which was very reasonable
先行词是时间 on which = when
先行词是地点 in which = where
先行词是原因 for which = why
- 进行时原型是=> be doing
- of + 名词
- the + 形容词 + 名词
- very + 形容词
- a few + 名词
- be + 形容词 / doing / ed(done)
- stop doing / to do
定语从句是修饰限定 名词 的,特殊情况前面有逗号就修饰 整个句子
名词性从句
==缺不缺 疑不疑==
找动词,画从句,分析成分,看含义
明明是句子但是却扮演的是名词,带了个帽子。人头上带了个柱子,现在充当柱子的成分,但是不能把这个帽子摘掉。无论是否有没有含义,都不能把这个帽帽去掉,否则就不能为柱子的成分。
让他带上这个帽子句子可以做主语是我的决定
[主语不是名词就是句子] [给那个句子带上一顶帽子 就变成了名词性从句]
句子带帽子后伪装成名词
名词从句的功能相当于名词词组
名词性从句:主语从句、宾语从句、表语从句、同位语从句
连接词:
that[不缺成分,没有含义],
if[不缺成分,有含义”是否”] = whether[不缺成分,含义”是否”]
whether能够放在句首引导主语从句;if不能;
whether能够放在介词之后引导宾语从句;if不能;
whether能够引导表语从句;if不能;
whether能够引导同位语从句;if不能;
==if只能引导动词后接的宾语从句和不位于句首的主语从句==
不缺成分,有含义
连接副词:when 何时 where 何地 how 怎样 why 为什么
缺成分,有含义
连接代词:
| what | 什么 | 主语和宾语 |
|---|---|---|
| who | 谁 | 主语和宾语 |
| whom | 谁 | 宾语 |
| which | 哪个 | 宾语(无成分) |
| whose | 誰的 | 定语(无成分) |
@@ I know what I can do缺宾语.
| 连接词 | 连接词 | 含义 | 成分 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 连接代词 | whom, whose, who/whoever, what/whatever, which | 有含义 | 主语、表语、宾语、定语(无成分) |
| 连接副词 | why, when, where, how | 有含义 | 状语(无成分) |
| 连接词 | that | 无含义 | 无成分 |
| 连接词 | whether, if | 有含义 | 无成分 |
主语从句[找动词,画从句,分析成分,看含义]
〇 ==一强二定三名词== [如果空前有动词就不能定]
句子不能直接做主语,要带帽帽
明天是否放假对我们是好事
Whether we have a holiday tomorrow is good for us
It good for us that whether we have a holiday tomorrow
==选帽子:缺不缺,疑不疑==
引导主语从句的连词主要有:that whether 疑问词
@@ (That you didn’t go to see the film) is a pity. [you didn’t go to see the film[句子不能做主语]作主句不合适 需要带帽子That 变成一个符合的从句 不可以省略,扮演了一个承接的角色]
缺不缺,疑不疑:you didn’t go to see the film 后面不缺主语;整个句子没有疑问,没有疑惑
① ==不缺不疑用That==
@@ It is a pity that you didn’t go to see the film.
**倒装的原因**:1.强调 2.脑袋太大(主语太长) -> [用it做形式主语 剩下的词一字不差的丢到后面去]
@@ (Whether you succeed or not) doesn’t interest me.
@@ It doesn’t interest me whether you succeed or not.
@@ That the earth is round (地球是圆的) is known to all.
@@ It is known to all that不可以省 the earth is round. [低调奢华有内涵]
@@ That you missed this chance (你错过了这次机会) is a pity.
考帽帽题!!一强用金三角扣掉看是否为一句话二定三名词 [如果前面没名词/先行词 那肯定不是定语从句] ==不缺不疑用That==
能够做形式主语的只有It 找真正主语,就在后面找主语前面的**帽子 **[that you]
that引导的主语从句作主语,谓语用单数。That不缺不疑 (we need time) is obvious.
② 缺缺缺 ==What、which、who/whom==
当后面引导的成分缺少的时候,用what、which、who/whom,
==如果 缺少人用whom 缺少物 what 缺少人?物?给了选择范围 就which==
What (we need) is time [需要的是时间,time是物 用what]
What (he gave me) are单/复取决于后面的表语 two books. [給的是两本书,books是物 用what]
What引导的句子做主语时,谓语动词的单/复数 是由它后面决定
What you said yesterday is tight.
It is right what you said yesterday is tight.
③ ==其他==
==不缺有疑,缺啥给啥[缺原因给why,怎样how,地点where,什么时候when]==
先找谓语动词,==谓语动词找离着远的[没有帽子的]!!==
步骤:[找动词,画从句,[缺不缺 疑不疑] [不缺有疑,缺啥给啥]
Who will win近 the game is远 not clear.
Whether (he’ll be able to come) is not yet know还不知道呢,缺啥给啥 会不会来,是否会来
是否[我们要参加这次会议]主语很长仍未被决定。 【not decided 现在完成时 hasn’t not be decided】
Whether we will attend the meeting hasn’t been decided yet.
it is hasn’t been decided whether we will attend the meeting yet.
ever系列和疑问系列:what特指 whatever泛指,以此类推都通用
先找谓语动词,谓语动词找离着远的[没有帽子的]!!
② @@ What makes this shop different is that it offers more personal services.
③ @@ That不缺不疑 (I can pay back the help that people give me) makes me very happy.
① @@ It’s not clear 1 was responsible for the accident.
从句即是主语
谓语动词之前
That you take care of my pet moved me a lot.
Whether we will go for an outing tomorrow is unknown.
=> It is unknown if we will go for an outing tomorrow.
What 缺宾语we need are good doctors. [what构成”所”字句:我们所需的是好医生]
Where I spend my time is no business of yours. [我在哪里消磨时间不关你的事]
主语从句常考点:it作形式主语,真正主语置于句末
It is/was said/reported/believed… 据说/据报道/人们相信
It is said that the star will visit our school next week.
It + 及物动词(happens等) … 碰巧
It happens that Mr.Li passes by.
lt + be + 名词(名词词组) + that 从句
It is a fact that …表示”事实是…”
It is an honor that…表示”…非常荣幸”
It is common knowledge that…表示”…是常识”
It + be + 形容词 + that从句
lt is clear that…表示“很显然…”
lt is necessary that…表示“…是必须的”
It + be + 动词的过去分词 + that从句
lt is reported that..表示”据报道…”
lt has been proved that…表示”已证实.…”
lt’s said that…表示”据说…”
It + 不及物动词 + that从句
lt seems that… 表示”似乎…..”
lt happened that.. 表示“碰巧”
lt appears that… 表示”似乎…”
what 与that在引导主语从句时的区别
what引导主语从句时在从句中充当句子成分如主语、宾语、表语,而that不充当句子成分[不能省略]
@@ (What makes his shop different) is that it offers more personal services.
@@ In some countries, (what is called “equality”) does not really mean equal right, for all people.
宾语从句[陈述语序(引导词后面)]
作宾语的从句,放在动词或介词之后
一强二定三名词
动词后加帽帽,不考虑定语从句,直接名词性从句
==that做宾语从句时候 可以省略=={只有that!!} [直接跟在动词后面的时候]
如果跟在adj/短语后不可以省略
I heard that可省略 he joined the army.
==物是直接宾语 人是间接宾语==
She told直接 me间接宾语 that跟直接宾语可省略 she would accept my invitation.
引导词 + 主语 + 谓语 + 其他
==It可以作为形式宾语[主谓宾补]== [as it where]
一般有it as 80/90%就是答案
if考点:[主将从现(如果) 虚拟]
原因:因为脑袋太大了
我觉得他后面要宾语补足语很漂亮[补足宾语的]
宾语不是一个词,是一长串!
我觉得让这个小伙离开这个座位是一个明确的选择。用it作形式宾语
We thought [it宾语 good news补足语] that帽帽 the fog had finally gone[宾语从句(名词性从句)].
只要宾语是it 后面有帽帽 后面就是宾语从句,就可以用口诀 疑不疑。缺不缺
[宾语很长] 因为宾语补足语只能补一个词,所以只能转换为万能词it,后面为具体内容good news
if 和 whether的选用
==if表达是否 只能用在宾语从句[前面是动词]== [其余从句都不可以]
@@ the question is表语 whether this book is worth writing
==一句一位找谓语动词,两句一连,无连带帽==
If you are not free tomorrow, I’ll go without you.
从句作介词的宾语不能用if
I’m not interested in whether they’ll go or not.直接跟不定式连用,连词不能用if
从句是一般疑问句作动词的宾语,两者都可以用
Whether … or not搭配,不能用if
==doubt用于肯定句 => 疑问 if/whether==
==doubt用于否定、疑问 =>肯定 that==
选项有疑问词 疑问词在前面;How+形容词+主语
宾语从句的时态呼应
如果主句时态是现在时或将来时,从句谓语可根据句意需要而选择用任意种时态
他相信他的梦想总有一天会实现的.
He believes his dream will come true some day
请告诉我你昨天这个时候在干什么[you do what] [过去现在进行时]
Please tell me what you were doing at this time yesterday
主句是过去式 从句都往它的过去变一档
He told me. I am preparing for the exam.
He told me he was preparing for the exam.He told me. I have left my hometown for many years.
He told me he had left his hometown for many years.如果用客观真理,该用什么
The teacher told the earth is round.
情态动词不能脱离动词单独实现 may be that 是对的
谓语动词和介词之后
I think ( that you are an intelligent student.)
| 连接词 | 连接词 | 含义 | 成分 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 连接代词 | whom, whose, who, what, which | 有含义 | 主语、表语、宾语、定语(无成分) |
| 连接副词 | why, when, where, how[方式状语] | 有含义 | 状语(无成分) |
| 连接词 | that | 无含义 | 无成分 |
| 连接词 | whether[是否], if | 有含义 | 无成分 |
He is asking whether/if we will go to the party.
I want to know (who will teach us English next term.) 括号内是宾语从句,宾语从句中缺主语
Please tell me how I can lose my weight.
在demand, order, suggest, decide, insist, desire, request,command等表示要求、命令、建议、决定等意义的动词后,宾语从句常用 “**(should)+动词原形**”。
I insist that she (should) do her homework on time.
The commander ordered that troops (should) set off at once.
介词之后的宾语从句,不可用which或if连接,要分别用what或whether
- ==宾语从句是否定句时,连接词只用if,不用whether==
- ==宾语从句中的whether与or not直接连用whether不能换成if==
I don’t know whether or not the report is true. - ==介词后的宾语从句要用whether引导,whether可与不定式连用; 但引导条件从句时表如果,只能用if,
而不能用whether。==
否定转移:若主句谓语动词为think, consider, suppose,believe, expect, fancy, guess, imagine等.
其后的宾语从句若含有否定意义,否定词一般要转移到主句谓语上,从句谓语用肯定式。例如:
it可以作为形式宾语,真正的宾语从句置于句尾,尤其是在带复合宾语的句子中。例如:
We heard it that she would get married next month.
We must see to it that everything is on the right track.
He made it clear that she had nothing to do with him.
表语从句【缺不缺疑不疑 有特殊==下面标黄==】
be动词或系动词之后
表语从句就是修饰名词的一个句子,一般THAT引导
| 连接词 | 连接词 | 含义 | 成分 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 连接代词 | whom, whose, who, what, which | 有含义 | 主语、表语、宾语、定语(无成分) |
| 连接副词 | why, when, where, how[方式状语] | 有含义 | 状语(无成分) |
| 连接词 | that[完整不缺] | 无含义 | 无成分 |
| 连接词 | whether[是否], if | 有含义 | 无成分 |
看缺不缺主谓宾。看缺不缺含义
Our dream is that (we can travel to Turkey one day).
The problem is whether the new project will succeed.
The question is (who/whom we should trust).
The most pressing question is why she failed in the exam.
That is why we all support his idea.
The reason (why he failed)定语从句 is ( that he was too careless)表语从句
The reason (I didn’t attend the lecture) was simply that I got a bad cold that day.
“主+系+表”
the reason is that… 和 It is because
现象和原因取决于上下文,没有上下文的时候取决于常识
==the reason (why)
+句子… is that…====this/that/it is why
+(现象)/ because+(原因)====the reason for
+名词… is that…== 如果why后面跟的是一个名词的时候,就不能加why 变成forgive sb sth
@@ The question is that/whether/how缺啥给啥 we can make good preparation in such a short time.
@@ This is why现象 we can’t get the support of the people.
@@ But the fact remains that we are behind the other classes.
@@ The reason why he is late for school is that he missed the early bus.
@@ This is where she was born.
@@ 看题目答案中是否有时态语态:by/虚拟信号词[advice] + (should) do
同位语从句 [不缺能连上是同位语]【缺不缺疑不疑】
名词或代词之后,进一步说明、解释它的情况
if不能引导同位语从句
一强二定连字诀[能直接连上就是定语从句],[直接/加介词也连不上就当名词从句做]三名词缺不缺,疑不疑
【后面缺成分就是定语从句 不缺成分的就是名词性从句】
He had the feeling that he could not see her again.
The question whether it is right or wrong depend on the result.
I have no idea when he will come back.
同位语从句,通常跟在一些抽象的名词之后[中间没有系动词 有系动词的是表语从句]
==hope / wish / fact / answer / problem / news /
belief / idea / promise / suggestion / order /
conclusion / information / thought==
They came to the conclusion that not all things can be done by a computer.
The fact that he had not said anything surprised everybody.
在suggestion、advice、request、order等意为“建议,命令,要求”的名词后,同位语从句中的谓语动词通常用”should+动词原形”的虚拟语气结构,句中的should可以省略。==demand、proposal、advice、suggestion唯独定语从句不能用虚拟该用啥用啥连字诀;若词后的是同位语从句,则 should + do,==
His order (that we arrive on time) is appropriate.主系表
他让我们准时到达的要求是合理的
==引导同位语从句的that不能省略==
The idea that (you can do this work well without thinking is quite wrong.)
你认为不动脑筋就能做好这份工作的想法是完全错误的。
==whether可以引导同位语从句,但是if不能引导同位语从句==
He must answer the question whether he agrees to or not.
状语从句【①~⑦】
铭升教育 ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓ ↓
[如果连词没了 啥也不能干了 变非谓语变太监先考虑是不是目的状语todo]
状语从句的存在环境:[有连词 无主语 有主语 无连词 连词主语一起没有]=>变太监,非谓语从句
① Hearing the bad news**,** they couldn’t help crying. [有逗号 两句一连 没连词 没主语,动词变太监] [目的todo 不是ing 就是ed 没主语说明主语就是后面的they 他们听到,他们主动听到ing]When they heard the bad news they couldn’t help crying.
= On hearing the bad news, they couldn’t help crying.
② While playing前面没she主语,因为后面爹一样 the piano, she got very excited. [一句一谓,两句一连,无连带帽,无帽变太监。有连词 没主语 只要缺一个就变太监、目的todo 不是ing 就是ed]
= While she was playing the piano, she got very excited.
连词,需要让别人知道自己是什么成分
③ Having turned off the radio, he began to go over his lessons.
= After he had turned off the radio, he began to go over his lessons.
= After turning off 有连词无主语,没有主语要变太监 the radio, he began to go over his lessons. [ing ed是哪个 看后面的主语 he 主动关掉]
④ As he forgot留意词本身 his manners, he put his feet up on the desk
[只要不是目的状语todo 清一色都是ing 、ed]
= Forgetting his manners, he put his feet up on the desk
⑤ because he was so angry, he couldn’t go to sleep.
= Being so angry, he couldn’t go to sleep.
⑥ Because (As) he had been to the Great Wall many times, he didn’t go last week.
= Having been to the Great Wall many times, he didn’t go last week.
⑦ If they had been given more attention the trees could have grown better.
= Given more attention, the trees could have grown better.
放句首时 不变
supposing、considering、including、according to、granted
Generally speaking… 一般来说
Frankly speaking…
Judging from…
Considering…
==当确认有连词皇帝的答案是错的时候,才考虑非谓语太监==
She set out soon after dark and arrived home an hour later.
A. arriving B. to arrived C. having arrived D. and arrived
D选项相当于省略了一个She 【先谓语,后非谓语 如果没有D选项 答案就是A选项】
如果是感官动词 要考虑是否为宾补是否完整,逻辑主语跟宾语相关
感官/使役类动词 后面是sth 直接+done
see/watch/notice/observe/look at/listen to/feel/==make/let/have==使役类 后面均可,其余的都是 to do ;
==感官类/使役类动词 后面是sth 直接接done==[5%几率 除非文中告诉正在做]
感官/使役类动词 可以省略to
目的状语放在后面的时候 中间不能有逗号
作宾语补足语 ==find leave get keep 三个都可以跟,但跟to do后面的to不能省略==
先进入房间后发现 Having entered
进入房间发现 Entering
Give blood if you can谓语但是前面有帽帽,所以是从句,不是真正谓语 and many lives will be saved.
找动词 找帽帽 找连词
有帽帽/连词的都是从句
有逗号 两句一连 没连词 没主语,动词变太监非谓语动词
↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑↑
no matter what
==状语从句是起着副词的作用的组词,用来修饰动词,副词和形容词==
状语从句:时间、让步、原因、条件、地点、目的、结果、方式、比较状语从句
时间状语从句:When she saw this, her face turned red.
原因状语从句:He was angry because I was late
条件状语从句:If you come, he’ll be pleased
结果状语从句:He was so angry that he couldn’t speak.
让步状语从句:Although he is poor, he’s happy.
方式状语从句:You must do as I tell you.
地点状语从句:Put it where you can reach it.
目的状语从句:Walk slowly so that he can follow you.
脱离了状语从句的主句,自己也能独立,意思不受影响;但~如果有状语从句会更好,信息量增加了, 整个句子的表达更加丰富:比如,你跟朋友八卦一件事的时候,就可以用状语从句,让TA知道这件事发生的时间、地点、原因、结果、企图等等;这个从句在句子结构里面的成分为宾语,主语,定语等成分。所以状语从句就是起到状语的作用。状语起到的作用类似于副词的作用,这样应该是比较好理解的。所以状语从句也分了很多种,比如时间状语从句,原因,条件等等。
时间状语从句
==when, while, as 当…时候;till/until 直到…;not…till/until 直到…才…
before 在…之前;after 在…之后;since 自从
as soon as, the moment, the minute, the instant 一…就…==
when、while
when 既可以接短暂性动词,也可以接延续性动词,表示从句动作与主句动作同时发生
while 表示“当…的时候”强调主句的动作和从句的动作同时发生,**从句一般用进行时,从句动词必须是延续性动词**
till/until 直到…,not…till/until 直到…才
till / until用于肯定句中,常与表示连续性的动词连用
not …till / until,常与表示短暂性动词连用
as soon as, the moment, the minute, the instant 一…就
no sooner… than…/hardly… when…/scarcely… when…(刚…就…)等
让步状语从句[退一步说]
==though, although, as,虽然/尽管
in spite of, despite 尽管
even if, even though,即使
while虽然、尽管(用于句首); 然而(用于句中)
however, whatever, wherever,whenever,whoever
(无论怎样/什么/哪里/时候/是谁)==
Tough he is a child, he knows a lot.
Whatever(= no matter what) you say, I’ll never change my mind.
though, although, as,虽然/尽管
Though / Although he is old, he works hard
= Old as he is, he works hard.
虽然他年纪大了,但他工作很努力。
despite, in spite of + 名词”尽管”
Despite/In spite of his old age,he works hard
no matter what = whatever(无论什么)
no matter how = however(无论怎样)
no matter who = whoever(无论怎样)
原因状语从句
because/as/for/since[自从] (因为)
considering (that) / given (that) (考虑到)
since/now that(既然) seeing(that) (由于,鉴于)
Now that you are here, you’d better stay. 你既然来了,最好还是留下吧。
Seeing that nobody was at home, I had to leave. 由于没人在家,我也只好走了
条件状语从句
if(如果,假设),in case(如果)
on condition (that)(如果,条件是…)
provided/providing that = suppose/supposing (that) 假如
I will go to the party on condition that she’s going too.
如果她参加聚会,我就参加
only if(只要,除非);as/so long as(只要)
I will go traveling with you as long as you pay.
I will go only if you go with me = I won’t go unless you go with me.
地点状语从句
where,wherever = no matter where
everywhere,anywhere等
I’ll go where you go. 你去哪我就去哪
目的状语从句
so that/in order that(为了)
in case(以防万一);lest/for fear that(以防)
in case后面跟着不想要的结果
so that后面跟着想要的结果
She left early in case she should miss the train.
结果状语从句
so that(因此,所以)
so/such…that… (如此…以至于…)
so + adj/adv + that…
so + adj/adv + a/an + cn单数 + that…
She is so tall that I envy her.
She is so tall a girl that I envy her.
方式状语从句
描述主句动作进行方式
as(按照),as if/as though(好像),the way(用…的方法),like(像…一样)
as if/as though 引导的状语从句 谓语多用虚拟语气,表示与事实相反,有时也用陈述语气,表示实现的可能性较大
He acted as if nothing had happened.他的举动好像什么事情都没有发生过
as if 引导的从句用相应的过去时表示虚拟语气
比较状语从句
形容词和副词的比较
① 原级比较:
as+形容词或副词原级+as
not+as/so+形容词或副词原级+as
我和这个可爱的猪猪一样胖
I am as fat as the cute pig.
I am not as fat as the cute pig.
② 两者比较:形容词或副词的比较级 + than 比…更…
可爱的猪猪比我更胖
The cute pig is fatter than me.
③ 形容词或副词比较级and形容词或副词比较级
more and more / less and less +形容词或副词原级 “越来越…”
bigger and bigger more and more beautiful
④ the形容词或副词的比较级,the形容词或副词的比较级:”越…, 就越…“
吃的越多长得越胖
The more you eat, the fatter you get.
⑤ 三者及以上的比较:“**the + 最高级 + 名词 + 表示比较范围**”
The Yangtze River is the longest river in China。
长江是中国最长的河流。
总结!!!!
(1) 在时间和条件(有时也在方式、让步等)从句中,主句是一般将来时,从句通常用一般现在时表示将来。(主将从现)
We’ll go outing if it doesn’t rain tomomrow.
如果明天不下雨,我们就会出去
I’ll write to you (as soon as I get to Shanghai.)
我一到上海就给你写信。
(2) 有些时间、地点、条件、方式或让步的从句,如果从句的主语与主句主语一致(或不一致,是be),从句的谓语又包含动词be,就可以省略从句中的”主语+be”部分
If (you are) asked, you may come in.
如果被叫到,你就可以进来。
If (it is) necessary, I’ll explain to you again.
如果有必要的话,我会再给你解释一遍。
since[自从,因为,既然] while[当…的时候,虽然,尽管;然而]
as[当…的时候,因为,尽管,按照,和…一样]
so that[得到的结果/目的] [因此,所以;为了,以便]
铭升教育
一句一谓,两句一连,无连带帽,不带帽变太监
后置定语只能放在名词后面变成to do【2个或者两个以上】
非谓语动词做定语 如果只有一个词的时候可以放在名词的前面
动名词ing,分词ed/ing,放在前面;放在后面 动词不定式,超过一个词的动名词和分词
如果动词有实际含义的词[笑、哭、走、跑]它就会有正在做的ing[主动或且正在进行] 被做的ed[被动或且完成时]
被动完成/主动完成 变成了两个词 变长了 放在后面 => 那个小男孩正在被打 [The little boy is being beaten]
抽象概念[鼓励、厌烦…]做定语 => ing修饰物,ed修饰人
后置的要超过两个词,≥2个词,后置后逻辑主语是名词。
==要做没做to do 正在做doing 被动完成 done 习惯做 to do 习惯性做to do==
动词不定式作定语
He was the last one (to leave school) yesterday. 主动离开学校
We have much homework to do everyday. ==Have sth to do…
